AMD Ryzen Threadripper 5000 Series "Genesis Peak" Processor Lineup Could Begin with a 16-Core Model
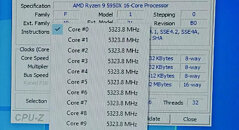
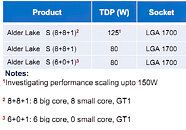
AMD is set to introduce its next-generation of Ryzen Threadripper processors in the coming weeks, and rumors are suggesting that it may happen at this year's CES. The new Ryzen Threadripper platform is codenamed Genesis Peak. If we take a look at the current 3000 series "Castle Peak" Threadripper processors, they were launched on CES 2020, with availability in February. So we are assuming that the upcoming 5000 "Genesis Peak" series is going to launch at the virtual CES event, during AMD's show. Thanks to the information from Yuri "1usmus" Bubliy, we found out that AMD is going to start the next-generation Threadripper lineup with a 16 core processor. "1usmus" posted a riddle on Twitter, that is actually a hex code that translates to "GENESIS 16 CORES".
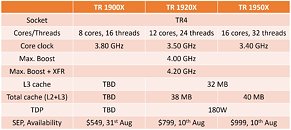
The current generation of Threadripper Castle Peak processors is starting at 24 cores, and going up to 64-core models, so it would be interesting to see where AMD sees the 16-core model in the stack and why it chose to do it. The exact specifications of this processor are unknown, so we have to wait for the announcement event. It is also unknown if the existing TRX40 motherboard will offer support for Zen 3 based Genesis Peak 5000 series Threadripper processors or will AMD introduce a new platform for it.
The current generation of Threadripper Castle Peak processors is starting at 24 cores, and going up to 64-core models, so it would be interesting to see where AMD sees the 16-core model in the stack and why it chose to do it. The exact specifications of this processor are unknown, so we have to wait for the announcement event. It is also unknown if the existing TRX40 motherboard will offer support for Zen 3 based Genesis Peak 5000 series Threadripper processors or will AMD introduce a new platform for it.