Intel Raptor Lake-S Cache Sizes Confirmed in Blurry CPU-Z Screenshot: 68MB L2+L3
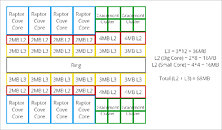
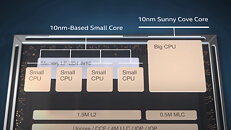
Back in January, we heard the first reports of Intel significantly increasing the on-die cache sizes on its 13th Gen Core "Raptor Lake-S" desktop processor, with the sum total of L2 and L3 caches on the silicon being 68 MB. A CPU-Z screenshot from the same source as the January story, confirmed the cache sizes. The "Raptor Lake-S" die in its full configuration features eight "Raptor Cove" performance cores (P-cores), and sixteen "Gracemont" efficiency cores (E-cores), making it a 24-core/32-thread chip.
Each "Raptor Cove" P-core features 2 MB of dedicated L2 cache even in its client variant, as previously reported, which is an increase from the 1.25 MB L2 cache of the "Golden Cove" P-cores on "Alder Lake-S." The sixteen "Gracemont" E-cores are spread across four E-core clusters, just like the eight E-cores of "Alder Lake-S" are spread across two such clusters. The four cores in each cluster share an L2 cache. Intel has doubled the size of this L2 cache from 2 MB on "Alder Lake" chips, up to 4 MB. The shared L3 cache on the silicon has increased in size to 36 MB. Eight P-cores with 2 MB each, and four E-core clusters with 4 MB, each, total 32 MB of L2 cache. Add this to 36 MB of L3 cache, and you get 68 MB of L2+L3 cache. Intel is expected to debut "Raptor Lake" in the second half of 2022 alongside the 700-series chipset, and backwards compatibility with 600-series chipset. It could go down as Intel's last client processor built on a monolithic silicon.
Each "Raptor Cove" P-core features 2 MB of dedicated L2 cache even in its client variant, as previously reported, which is an increase from the 1.25 MB L2 cache of the "Golden Cove" P-cores on "Alder Lake-S." The sixteen "Gracemont" E-cores are spread across four E-core clusters, just like the eight E-cores of "Alder Lake-S" are spread across two such clusters. The four cores in each cluster share an L2 cache. Intel has doubled the size of this L2 cache from 2 MB on "Alder Lake" chips, up to 4 MB. The shared L3 cache on the silicon has increased in size to 36 MB. Eight P-cores with 2 MB each, and four E-core clusters with 4 MB, each, total 32 MB of L2 cache. Add this to 36 MB of L3 cache, and you get 68 MB of L2+L3 cache. Intel is expected to debut "Raptor Lake" in the second half of 2022 alongside the 700-series chipset, and backwards compatibility with 600-series chipset. It could go down as Intel's last client processor built on a monolithic silicon.