Intel 12th Gen "Alder Lake" Mobile CPUs Face Retirement, HX-series Spared
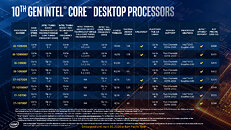
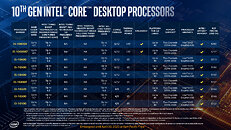
Intel product change notification documents—published on January 6—have revealed the planned "End of Life" (EOL) phasing out of 12th Generation "Alder Lake" mobile processor models. Tom's Hardware has pored over the listed products/SKUs and concluded that the vast majority of Team Blue's mobile-oriented Alder Lake selection are destined for retirement. Team Blue's HX series is being kept alive for a little while longer. Two documents show differing "discontinuance timelines" for their respective inventories—including lower-end Celeron and Pentium Gold SKUs, as well as familiar higher-up Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 families. U, P, H and HK-affixed models are lined up for the chopping block.
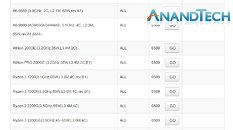
Intel's 13th Generation "Raptor Lake" mobile processor selection—comprised of Core 100 (series 1) and Core 200 (series 2)—offers similar silicon makeup. Many equivalent alternatives to older generation "Alder Lake" chips reside here—Tom's Hardware presented a key example: "i5-1235U, which is designated for thin and lightweight laptops. OEMs can instead opt for the i5-1335U, the Core 5 120U, or the Core 5 220U, as they're just better bins of the 1235U on the same FCBGA1744 socket." A significant number of Alder Lake mobile SKUs will be available to OEMs for ordering up until 26 April, with final shipments heading out on 25 October. The rest have been assigned a July 25 order cut-off date, with final shipments scheduled on 26 January 2026.
Intel's 13th Generation "Raptor Lake" mobile processor selection—comprised of Core 100 (series 1) and Core 200 (series 2)—offers similar silicon makeup. Many equivalent alternatives to older generation "Alder Lake" chips reside here—Tom's Hardware presented a key example: "i5-1235U, which is designated for thin and lightweight laptops. OEMs can instead opt for the i5-1335U, the Core 5 120U, or the Core 5 220U, as they're just better bins of the 1235U on the same FCBGA1744 socket." A significant number of Alder Lake mobile SKUs will be available to OEMs for ordering up until 26 April, with final shipments heading out on 25 October. The rest have been assigned a July 25 order cut-off date, with final shipments scheduled on 26 January 2026.