Haswell-ULT Processors Could Use 24 MHz BClk, New C-States, and MCM to Cut Power Draw
Going into 2013, Intel's tough balancing act between keeping a low power/thermal envelope, and advancing performance, all while staying on the 22 nm silicon fab process, will be care of its Core "Haswell-ULT" processor. The chip will feature some radical changes to traditional Intel processor design, which will help it achieve its design goals. According to a deck of leaked slides scored by Expreview, Intel plans to use additional C-states that drop the processor's base clock, and redesign the processor package to accommodate the PCH silicon, reducing the board footprint.
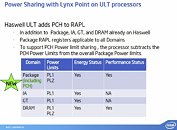
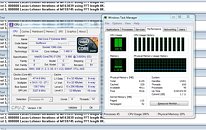
To begin with, Haswell-ULT will be designed to support 24 MHz base clock speed, which running in "deep" energy-saving idle states. Modern processors with FSB replacement interconnect technologies such as QuickPath Interconnect and HyperTransport need a base clock to time other components on the processor, and for low-level communications, while a bulk of the data is transported by the primary interconnect. Intel found a way to turn off the 100 MHz base clock signal (which is also used to time the PCI-Express root complex and integrated graphics core), and replace it with a 24 MHz clock, when the processor is idling. As the processor returns to lower (more active) C-states, the 100 MHz base clock is reapplied. The 24 MHz base clock is activated by three new power states, C8, C9, and C10, introduced by Haswell-ULT. The third slide below details what happens to the various components in the new C-states.
To begin with, Haswell-ULT will be designed to support 24 MHz base clock speed, which running in "deep" energy-saving idle states. Modern processors with FSB replacement interconnect technologies such as QuickPath Interconnect and HyperTransport need a base clock to time other components on the processor, and for low-level communications, while a bulk of the data is transported by the primary interconnect. Intel found a way to turn off the 100 MHz base clock signal (which is also used to time the PCI-Express root complex and integrated graphics core), and replace it with a 24 MHz clock, when the processor is idling. As the processor returns to lower (more active) C-states, the 100 MHz base clock is reapplied. The 24 MHz base clock is activated by three new power states, C8, C9, and C10, introduced by Haswell-ULT. The third slide below details what happens to the various components in the new C-states.