Radeon VII Lacks Full FP64 Compute Capabilities Available to Instinct MI60
AMD's upcoming Radeon VII high-end consumer graphics card lacks full FP64 compute capabilities available to the company's other products targeting the enterprise-compute market, such as the Radeon Instinct MI60. Radeon VII offers an FP32 peak compute throughput of 13.8 TFLOP/s single-precision, which, given its hardware resources, should normally work out a double-precision throughput of 6.7 TFLOP/s. However, with the feature disabled for the Radeon VII, the FP64 throughput will be closer to 860 GFLOP/s. Disabling FP64 capabilities for client-segment graphics cards is a common practice among both AMD and NVIDIA.
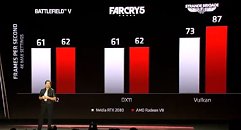
For gamers, PC enthusiasts, and even creative professionals, double-precision floating-point performance of a graphics card remains completely irrelevant. The disabling of DPFP ensures gamers have access to Radeon VII, lest every cloud compute provider and their dog would soak up Radeon VII inventory owing to its $699 list price, had it offered 6.7 TFLOP/s rivaling compute accelerators 10-15 times more. Radeon VII is the world's first consumer graphics processor built on the 7 nm silicon fabrication process, with company-claimed performance rivaling NVIDIA's RTX 2080. It will be available from February 7.
For gamers, PC enthusiasts, and even creative professionals, double-precision floating-point performance of a graphics card remains completely irrelevant. The disabling of DPFP ensures gamers have access to Radeon VII, lest every cloud compute provider and their dog would soak up Radeon VII inventory owing to its $699 list price, had it offered 6.7 TFLOP/s rivaling compute accelerators 10-15 times more. Radeon VII is the world's first consumer graphics processor built on the 7 nm silicon fabrication process, with company-claimed performance rivaling NVIDIA's RTX 2080. It will be available from February 7.