Intel Rocket Lake CPUs Will Bring up to 10% IPC Improvement and 5 GHz Clocks
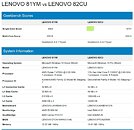
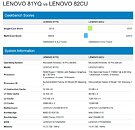
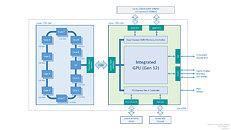
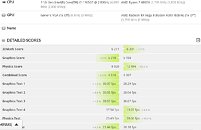
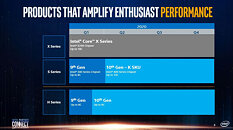
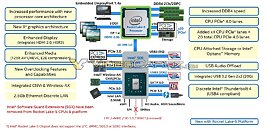
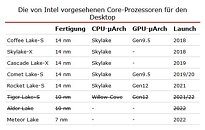
Intel is struggling with its node development and it looks like next-generation consumer systems are going to be stuck on 14 nm for a bit more. Preparing for that, Intel will finally break free from Skylake-based architectures and launch something new. The replacement for the current Comet Lake generation is set to be called Rocket Lake and today we have obtained some more information about it. Thanks to popular hardware leaker rogame (_rogame), we know a few stuff about Rocket Lake. Starting off, it is known that Rocket Lake features the backport of 10 nm Willow Cove core, called Cypress Cove. That Cypress Cove is supposed to bring only 10% IPC improvements, according to the latest rumors.
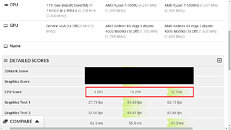
With 10% IPC improvement the company will at least offer some more competitive product than it currently does, however, that should be much slower than 10 nm Tiger Lake processors which feature the original Willow Cove design. It shows that backporting of the design doesn't just bring loses of the node benefits like smaller design and less heat, but rather means that only a fraction of the performance can be extracted. Another point that rogame made is that Rocket Lake will run up to 5 GHz in boost, and it will run hot, which is expected.
With 10% IPC improvement the company will at least offer some more competitive product than it currently does, however, that should be much slower than 10 nm Tiger Lake processors which feature the original Willow Cove design. It shows that backporting of the design doesn't just bring loses of the node benefits like smaller design and less heat, but rather means that only a fraction of the performance can be extracted. Another point that rogame made is that Rocket Lake will run up to 5 GHz in boost, and it will run hot, which is expected.