Goldman Sachs Upgrades Stock Ratings for AMD, Downgrades Intel to "Sell"
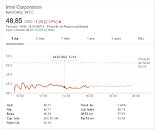
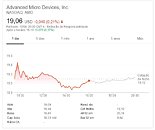
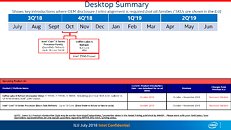
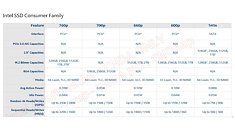
Goldman Sachs, citing problems with Intel's 10 nm manufacturing process delivery - which was supposed to be available in the market for years now - has reduced the blue giant's stock rating. Previously at a "neutral" stance - already downgraded in the face of Intel's manufacturing woes - the stock is now at a "Sell" level. Even though Intel is still outperforming the S&P 500's 6.7 percent return with their (current) 8.6 percent this year through Thursday, the outlook isn't good for the company.
"We see Intel's struggles with 10 nm process technology having ramifications in terms of its competitive position - across a broad set of products. While the 10nm push is well-publicized at this point, we believe Intel's manufacturing issues could potentially be deeper-rooted than what most think and could have a sustained impact on market share and/or spending levels as Intel competes with a growing/stronger TSMC eco-system."
Goldman Sachs Analyst Toshiya Hari