Thursday, August 12th 2010

Toshiba Introduces Double Data Rate Toggle Mode NAND In MLC And SLC Configurations
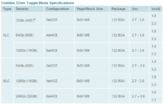
Toshiba America Electronic Components, Inc ., (TAEC) is introducing 32 nm double data rate Toggle Mode NAND, in multi-level cell (MLC) versions with densities of 64 Gb, 128 Gb and 256 Gb and single-level cell (SLC) versions with densities of 32 Gb, 64 Gb and 128 Gb. Toggle Mode NAND features a faster interface than conventional or "legacy" asynchronous NAND memory with lower power consumption than competing synchronous DDR NAND product offerings.
Toshiba DDR Toggle Mode 1.0 NAND has a fast interface rated at 133 megatransfers per second (MT/s), compared to 40 MT/s for legacy SLC single data rate NAND, which makes it suitable for high performance solid state storage applications including enterprise storage. Since it uses an asynchronous interface similar to that used in conventional NAND, the Toshiba DDR Toggle Mode NAND requires no clock signal, which means that it uses less power and has a simpler system design compared to competing synchronous NAND alternatives. The DDR interface in Toggle Mode NAND uses a Bidirectional DQS to generate input/output signals (I/Os) using the rising and falling edge of the write erase signal. Toggle Mode NAND also has on-die termination to help achieve less crosstalk.
Scalability to future high-frequency operation is enabled as a result of the bi-directional data signal. Toshiba recently announced a commitment to a new standard for the most advanced high-performance NAND flash memory, a DDR NAND flash with a 400Mbps3 interface. This next generation Toggle Mode DDR NAND 2.0 is targeted to provide a three-fold increase in interface speed over Toggle DDR 1.0 and a ten-fold increase over the 40Mbps single data rate NAND in widespread use today.
Toshiba Toggle Mode NAND supports common legacy NAND commands including basic, multi-plane and cache operations.
Toshiba DDR Toggle Mode 1.0 NAND has a fast interface rated at 133 megatransfers per second (MT/s), compared to 40 MT/s for legacy SLC single data rate NAND, which makes it suitable for high performance solid state storage applications including enterprise storage. Since it uses an asynchronous interface similar to that used in conventional NAND, the Toshiba DDR Toggle Mode NAND requires no clock signal, which means that it uses less power and has a simpler system design compared to competing synchronous NAND alternatives. The DDR interface in Toggle Mode NAND uses a Bidirectional DQS to generate input/output signals (I/Os) using the rising and falling edge of the write erase signal. Toggle Mode NAND also has on-die termination to help achieve less crosstalk.
Scalability to future high-frequency operation is enabled as a result of the bi-directional data signal. Toshiba recently announced a commitment to a new standard for the most advanced high-performance NAND flash memory, a DDR NAND flash with a 400Mbps3 interface. This next generation Toggle Mode DDR NAND 2.0 is targeted to provide a three-fold increase in interface speed over Toggle DDR 1.0 and a ten-fold increase over the 40Mbps single data rate NAND in widespread use today.
Toshiba Toggle Mode NAND supports common legacy NAND commands including basic, multi-plane and cache operations.
2 Comments on Toshiba Introduces Double Data Rate Toggle Mode NAND In MLC And SLC Configurations