Way back in June 2018, when the first Threadrippers made landfall, it
was reported that Intel was working on a new 22-core "Skylake-X" silicon that sat in between the 18-core HCC (high core-count) die, and the 28-core XCC (extreme core-count) die. The roughly 700 mm² XCC die, with its 6 memory channels, couldn't be integrated with the LGA2066 package, and was reserved for the enterprise LGA3647 package that made a workstation/quasi-client debut with the 28-core Xeon W-3175X. It was hence rumored that an in-between 22-core silicon was under development that could be integrated with LGA2066. Fast forward to 2020, and Intel's client HEDT processor lineup doesn't look much different from its 2017 one. The 18-core i9-10980XE leads the pack, and despite its $1,000 price, has received largely lukewarm reviews. If screenshots surfacing on Chinese tech forums are to be believed, Intel is toying with the idea of the 22-core die meant for LGA2066 once again.
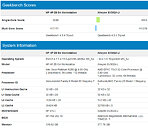
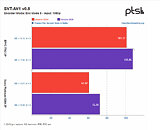
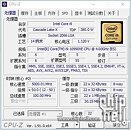
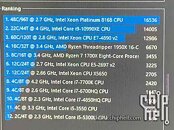
Referenced as Core i9-10990XE in straight-up CPU-Z screenshots, the processor is based on the "Cascade Lake-X" microarchitecture, and has the same I/O as the i9-10980XE, looking at the instruction sets featured. It has 22 cores and HyperThreading enables 44 threads. Cache hierarchy and balance are characteristic of "Cascade Lake," with 1 MB of dedicated L2 cache per core, and 30.25 MB of shared L3 cache. The I/O is likely identical to the i9-10980XE as that's a function of the platform and the socket. What's more interesting are the clock-speeds. The name-string of the engineering sample references a nominal clock-speed of 4.00 GHz, and in the screenshot, the chip is shown running at 5.00 GHz (at least on one core). There's also a performance benchmark to go with the leak, possibly CineBench R20 nT. Here, the i9-10990XE is shown scoring 14,005 points, which is in the same ballpark as the 24-core Ryzen Threadripper 3960X.