FFmpeg Gets NVENC AV1 Encode Support for a 75-100% Encoding Speed Uplift Over HEVC
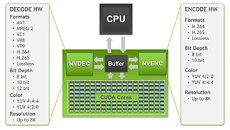
Popular video transcoding and playback software FFmpeg, in its latest update, received support for AV1 format hardware-accelerated encoding leveraging the NVENC AV1 hardware encoders on the latest NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40-series "Ada" GPUs. The author Timo Rothenpieler remarked that in his testing, the new NVENC AV1 encoder is outperforming the NVENC HEVC-based FFmpeg encoding by 75 to 100 percent, in terms of encoding speed, at comparable quality. When deployed at a data-center scale, or even a production studio-scale, accelerated AV1 encoding should have a tangible impact on costs, and not just because AV1 is a royalty-free format. NVENC AV1 encoding support was also recently added to OBS Studio, the popular free video streaming software.