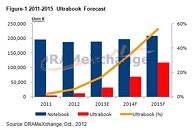
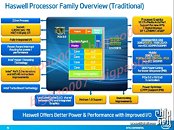
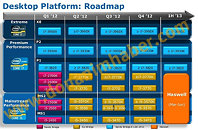
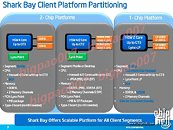
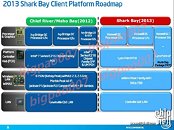
Some time in 2013, Intel will launch its new processor architecture, codenamed "Haswell", which will go on to succeed "Ivy Bridge". More than an year away from its market entry, Haswell has already been
exhaustively documented, but not many got into the details about its embedded graphics processor. That is, until now. A new internal slide sourced by DonanimHaber details the integrated GPU (iGPU), it appears like Intel has solid plans for home users.
To begin with, Haswell's iGPU will be DirectX 11.1 compliant, which means it will take advantage of API optimizations that improve performance, for typical desktop usage scenarios. Apart from support for a new DirectCompute architecture, it will also support OpenCL 1.2, which speeds up certain GPGPU-optimized applications. More importantly, the iGPU will be designed around a new stereoscopic 3D standard called Auto-Stereoscopic 3D (AS3D), which will take the likes of Blu-ray 3D acceleration, stereo 3D photos, etc., to the masses. Currently, it takes at least an entry-level GeForce or Radeon GPU to for acceptable performance with stereo 3D.