Intel Deploys Microcode Update for Spectre Flaw on Skylake
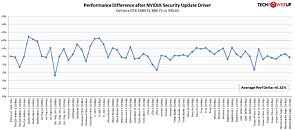
In another step of our Spectre/Meltdown odyssey, Intel has started deployment of a fixed update for its Skylake processors, which aims to neuter chances of a malicious attacker exploiting the (now) known vulnerabilities. This update, which comes after a botched first update attempt that was causing widespread system reboots and prompted Intel to change its update guidelines, is only for the Skylake platform; other Intel CPUs' updates remain in Beta state, and there's no word on when they might see a final deployment.
The new microcode is being distributed to industry partners, so that they can include it in a new range of firmware updates that will, hopefully, end the instability and vulnerabilities present in current mobile and desktop Skylake implementations. Users of other Intel architectures will still have to wait a while longer before updates for their systems are certified by Intel, distributed to industry partners, and then trickle to end users via firmware updates.
The new microcode is being distributed to industry partners, so that they can include it in a new range of firmware updates that will, hopefully, end the instability and vulnerabilities present in current mobile and desktop Skylake implementations. Users of other Intel architectures will still have to wait a while longer before updates for their systems are certified by Intel, distributed to industry partners, and then trickle to end users via firmware updates.