110°C Hotspot Temps "Expected and Within Spec", AMD on RX 5700-Series Thermals
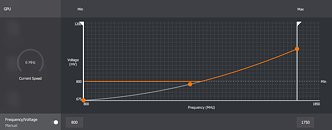
AMD this Monday in a blog post demystified the boosting algorithm and thermal management of its new Radeon RX 5700 series "Navi" graphics cards. These cards are beginning to be available in custom-designs by AMD's board partners, but were only available as reference-design cards for over a month since their 7th July launch. The thermal management of these cards spooked many early adopters accustomed to seeing temperatures below 85 °C on competing NVIDIA graphics cards, with the Radeon RX 5700 XT posting GPU "hotspot" temperatures well above 100 °C, regularly hitting 110 °C, and sometimes even touching 113 °C with stress-testing application such as Furmark. In its blog post, AMD stated that 110 °C hotspot temperatures under "typical gaming usage" are "expected and within spec."
AMD also elaborated on what constitutes "GPU Hotspot" aka "junction temperature." Apparently, the "Navi 10" GPU is peppered with an array of temperature sensors spread across the die at different physical locations. The maximum temperature reported by any of those sensors becomes the Hotspot. In that sense, Hotspot isn't a fixed location in the GPU. Legacy "GPU temperature" measurements on past generations of AMD GPUs relied on a thermal diode at a fixed location on the GPU die which AMD predicted would become the hottest under load. Over the generations, and starting with "Polaris" and "Vega," AMD leaned toward an approach of picking the hottest temperature value from a network of diodes spread across the GPU, and reporting it as the Hotspot.
AMD also elaborated on what constitutes "GPU Hotspot" aka "junction temperature." Apparently, the "Navi 10" GPU is peppered with an array of temperature sensors spread across the die at different physical locations. The maximum temperature reported by any of those sensors becomes the Hotspot. In that sense, Hotspot isn't a fixed location in the GPU. Legacy "GPU temperature" measurements on past generations of AMD GPUs relied on a thermal diode at a fixed location on the GPU die which AMD predicted would become the hottest under load. Over the generations, and starting with "Polaris" and "Vega," AMD leaned toward an approach of picking the hottest temperature value from a network of diodes spread across the GPU, and reporting it as the Hotspot.