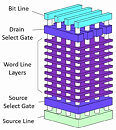
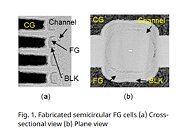
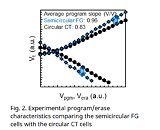
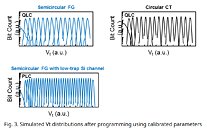
NEO Semiconductor X-NAND Standard Offers Performance Comparable to SLC at Costs of QLC, Wins FMS 2020 Best of Show
NEO Semiconductor was honored with a Flash Memory Summit 2020 Best of Show Award for Hardware Architecture at today's Flash Memory Summit 2020 Best of Show Awards ceremony. The Flash Memory Summit, the World's largest and most prestigious storage industry conference and exposition, recognizes NEO Semiconductor's X-NAND product solution.
"5G, robotics, virtual reality and AI applications demand the highest level of performance in order to meet the service level objectives of business-critical data center workloads," said Jay Kramer, Chairman of the Awards Program and President of Network Storage Advisors Inc. "We are proud to recognize NEO Semiconductor X-NAND product solution for providing an excellent high-performance solution that can uniquely lower the cost across all tiers of SSD technologies."
"5G, robotics, virtual reality and AI applications demand the highest level of performance in order to meet the service level objectives of business-critical data center workloads," said Jay Kramer, Chairman of the Awards Program and President of Network Storage Advisors Inc. "We are proud to recognize NEO Semiconductor X-NAND product solution for providing an excellent high-performance solution that can uniquely lower the cost across all tiers of SSD technologies."