PGL Upgrades Tournament Rigs - Selects AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D CPU
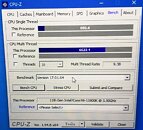
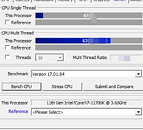
Last week, the Professional Gamers League (PGL) announced an interesting overhaul of tournament hardware—new systems will be fitted with NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4080 graphics cards, then hooked up to BenQ ZOWIE XL2566K 24.5" 360 Hz gaming monitors. Their previous generation machines were (initially) designed around AMD's Ryzen 9 5950X processor, but the organization is leaving AM4 platforms behind: "PGL is excited to announce that our team has fully optimized upgraded gaming PCs in partnership with Afromnazareth, and we are ready to deliver an unparalleled esports experience at the PGL CS2 Major Copenhagen 2024. At the heart of this cutting-edge setup is the AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D processor, explicitly chosen for its exceptional performance capabilities and ability to handle the demands of CS2. This processor is renowned for its superior gaming performance, offering players the speed, power, and efficiency required to perform at the highest levels of competition."
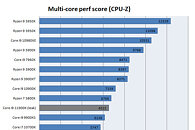
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D is a more straightforward upgrade—as an easy drop-in for the PGL's older AM4 platform machines, but a leap into new ecosystems will grant a bit of future-proofing. Team Red is expected to support AM5 across a couple of processor generations. PGL did upgrade systems with 5800X3D CPUs, due to player feedback—according to Tom's Hardware: "there was some discontent among players with the previous configuration with the Ryzen 9 5950X because, while the chip sports 16 Zen 3 execution cores, Counter-Strike 2 doesn't exploit the processor's prowess. Some players criticized PGL's poor processor choice for previous events, claiming lousy frame rates." Performance connoisseurs will be pleased to hear about the tournament organizer's new push into modern platforms—Silviu Stroie, PGL CEO, stated: "we have meticulously optimized this bespoke gaming setup to ensure that every participant experiences CS2 in the highest fidelity without compromise. The AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D CPU stands out as a game-changer in the esports arena, promising to elevate the competitive play of CS2 to new heights."
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D is a more straightforward upgrade—as an easy drop-in for the PGL's older AM4 platform machines, but a leap into new ecosystems will grant a bit of future-proofing. Team Red is expected to support AM5 across a couple of processor generations. PGL did upgrade systems with 5800X3D CPUs, due to player feedback—according to Tom's Hardware: "there was some discontent among players with the previous configuration with the Ryzen 9 5950X because, while the chip sports 16 Zen 3 execution cores, Counter-Strike 2 doesn't exploit the processor's prowess. Some players criticized PGL's poor processor choice for previous events, claiming lousy frame rates." Performance connoisseurs will be pleased to hear about the tournament organizer's new push into modern platforms—Silviu Stroie, PGL CEO, stated: "we have meticulously optimized this bespoke gaming setup to ensure that every participant experiences CS2 in the highest fidelity without compromise. The AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D CPU stands out as a game-changer in the esports arena, promising to elevate the competitive play of CS2 to new heights."