Noctua Extends Free Mounting Kit Offer and Confirms LGA1155 Compatibility
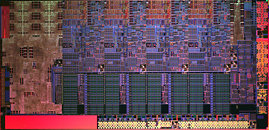
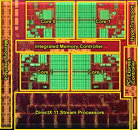
Noctua today announced that owners of older Noctua CPU coolers who wish to upgrade to the upcoming LGA1155 socket will be able to obtain the appropriate NM-I3 SecuFirm2 mounting kit free of charge. Recent models such as the NH-C14, NH-D14 or NH-U12P SE2 already include the NM-I3 mounting kit and are fully compatible with LGA1155 out of the box.
"We're determined to provide the best possible support to our customers and we've sent many thousands of NM-I3 mounting kits free of charge to users who wanted to upgrade to LGA1156", says Mag. Roland Mossig, Noctua CEO. "With Sandy Bridge just around the corner, we're pleased to announce that we'll extend this offer for LGA1155 users. Everyone owning an older Noctua heatsink that doesn't support LGA 115x out of the box will be able to upgrade to the new socket free of charge!"
"We're determined to provide the best possible support to our customers and we've sent many thousands of NM-I3 mounting kits free of charge to users who wanted to upgrade to LGA1156", says Mag. Roland Mossig, Noctua CEO. "With Sandy Bridge just around the corner, we're pleased to announce that we'll extend this offer for LGA1155 users. Everyone owning an older Noctua heatsink that doesn't support LGA 115x out of the box will be able to upgrade to the new socket free of charge!"