New "Spectre" Variant Hits Intel CPUs, Company Promises Quarterly Microcode Updates
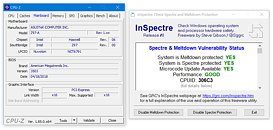
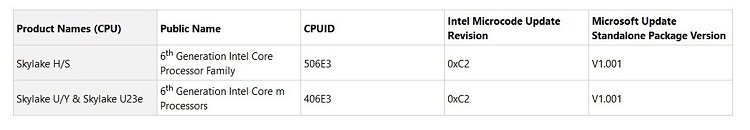
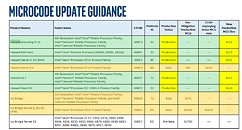
A new variant of the "Spectre" CPU vulnerability was discovered affecting Intel processors, by security researchers Vladimir Kiriansky and Carl Waldspurger, who are eligible to bag a USD $100,000 bounty by Intel, inviting researchers to sniff out vulnerabilities from its processors. This discovery, chronicled under CVE-2018-3693, is among 12 new CVEs Intel will publish later this week. The company is also expected to announce quarterly CPU microcode updates to allay fears of its enterprise customers.
The new vulnerability, like most other "Spectre" variants, targets the speculative execution engine of the processor, in a bounds-check bypass store attack. A malicious program already running on the affected machine can alter function pointers and return addresses in the speculative execution engine, thereby redirecting the flow of data out of protected memory address-spaces, making it visible to malware. This data could be anything, including cryptographic keys, passwords, and other sensitive information, according to "The Register." Intel chronicled this vulnerability in section 2.2.1 of its revised speculative execution side-channel attacks whitepaper. You can also catch a more detailed whitepaper from the researchers themselves.
The new vulnerability, like most other "Spectre" variants, targets the speculative execution engine of the processor, in a bounds-check bypass store attack. A malicious program already running on the affected machine can alter function pointers and return addresses in the speculative execution engine, thereby redirecting the flow of data out of protected memory address-spaces, making it visible to malware. This data could be anything, including cryptographic keys, passwords, and other sensitive information, according to "The Register." Intel chronicled this vulnerability in section 2.2.1 of its revised speculative execution side-channel attacks whitepaper. You can also catch a more detailed whitepaper from the researchers themselves.