Moore's Law Buckles as Intel's Tick-Tock Cycle Slows Down
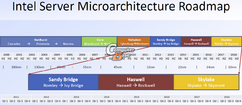
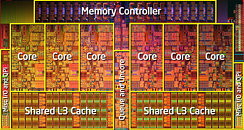
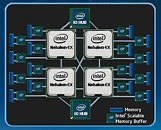
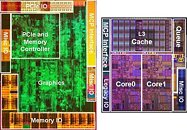
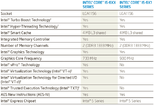
Intel co-founder Gordon Moore's claim that transistor counts in microprocessors can be doubled with 2 years, by means of miniaturizing silicon lithography is beginning to buckle. In its latest earnings release, CEO Brian Krzanich said that the company's recent product cycles marked a slowing down of its "tick-tock" product development from 2 years to close to 2.5 years. With the company approaching sub-10 nm scales, it's bound to stay that way.
To keep Moore's Law alive, Intel adopted a product development strategy it calls tick-tock. Think of it as a metronome that give rhythm to the company. Each "tock" marks the arrival of a new micro-architecture, and each "tick" marks its miniaturization to a smaller silicon fab process. Normally, each year is bound to see one of the two in alternation.
To keep Moore's Law alive, Intel adopted a product development strategy it calls tick-tock. Think of it as a metronome that give rhythm to the company. Each "tock" marks the arrival of a new micro-architecture, and each "tick" marks its miniaturization to a smaller silicon fab process. Normally, each year is bound to see one of the two in alternation.