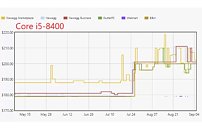
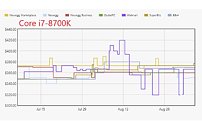
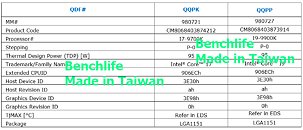
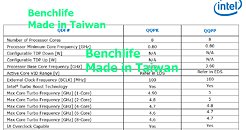
GIGABYTE Launches the Z390 Designare Motherboard
GIGABYTE TECHNOLOGY Co. Ltd, a leading manufacturer of motherboards and graphics cards, announced the release of the Z390 DESIGNARE motherboard with full support for the newest 8-core Intel Core i9-9900K processors. The newest addition to the GIGABYTE DESIGNARE series is a feature-packed motherboard that provides content creators the fastest and most efficient tools to showcase their creativity and craftsmanship. GIGABYTE DESIGNARE Series motherboards bring out the best in workstation graphics cards, maximize M.2 SSD and DDR4 RAM performance, and fully support powerful CPUs such as the newest 8-core Intel Core i9-9900K CPU. With built in USB Type-C Thunderbolt , and native USB 3.1 Gen 2 to provide 40Gb/s transmission speed, the board is designed with effective storage performance as a key feature. GIGABYTE Ultra-Durable Technology and exclusive software also bring additional value for digital content creators and design professionals.
"Today's content creators are seeking faster and more efficient performance from their PCs. GIGABYTE created the DESIGNARE series a few years back to fulfill these user demands," stated Jackson Hsu, Deputy Director of the GIGABYTE Channel Solutions Product Development Division. "Z390 DESIGNARE is the newest addition to this constantly evolving content creation focused series and is loaded with features that enable content creators to express their artistic creativity through their PCs with excellent performance and efficiency."
"Today's content creators are seeking faster and more efficient performance from their PCs. GIGABYTE created the DESIGNARE series a few years back to fulfill these user demands," stated Jackson Hsu, Deputy Director of the GIGABYTE Channel Solutions Product Development Division. "Z390 DESIGNARE is the newest addition to this constantly evolving content creation focused series and is loaded with features that enable content creators to express their artistic creativity through their PCs with excellent performance and efficiency."