TSMC N5P 5nm Node Offers 84-87% Transistor Density Gain Over Current 7nm Node
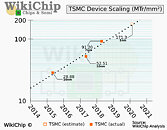
A WikiChip analysis of TSMC's next-generation 5 nanometer N5P silicon fabrication node estimates a massive 84-87% increase in transistor densities on offer compared to the company's first commercial 7 nm-class node, the N7 (7 nm DUV). The report estimates an 87% transistor-density increase, even though TSMC's own figure is slightly modest, at 84%. TSMC N5P node is expected to commence production later this year. Its precursor, TSMC N5, began risk production earlier this year, with production on the node commencing in April or May, unless derailed by the COVID-19 pandemic. The N5P node provides transistor densities of an estimated 171.3 million transistors per mm² die area, compared to 91.2 mTr/mm² of N7. Apple is expected to be the node's biggest customer in 2020, with the company building its A14-series SoC on it.