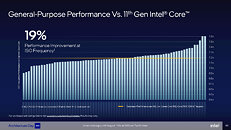
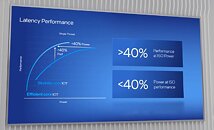
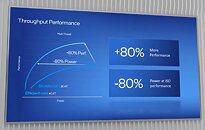
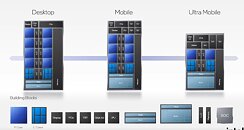
ASUS Z690 Motherboards Listed by Canadian Retailer
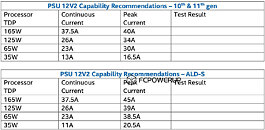
Intel is set to launch their 12th Generation Alder Lake desktop processors on November 4th alongside the new Z690 chipset supporting DDR5 and PCIe 5.0. We have recently seen the first of these new Z690 motherboards from ASUS being listed for sale by PC Canada. The listings include TUF, ROG Maximus, ROG Strix, and Prime motherboards but we don't see any mention of Apex or Extreme boards so they may not be available at launch. The models all appear to retail for less than their Z590 counterparts except for some of the Prime series models which will come as a pleasant surprise to many. We are also aware that the VRM design for these boards will receive various upgrades according to a recent report from @Komachi. The Z690 Hero is set to feature a 20+1 phase design with 90 A Power Stages while the lower-end boards will get a 14+1 design.