3DMark Speed Way DirectX 12 Ultimate Benchmark is Launching on October 12
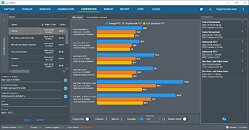
3DMark Speed Way is a new GPU benchmark that showcases the graphics technology that will power the next generation of gaming experiences. We're excited to announce Speed Way, sponsored by Lenovo Legion, is releasing on October 12. Our team has been working hard to get Speed Way ready for you to use benchmarking, stress testing, and comparing the new PC hardware coming this fall.
From October 12 onward, Speed Way will be included in the price when you buy 3DMark from Steam or our own online store. Since we released Time Spy in 2016, 3DMark users have enjoyed many free updates, including Time Spy Extreme, the 3DMark CPU Profile, 3DMark Wild Life, and multiple tests demonstrating new DirectX features. With the addition of Speed Way, the price of 3DMark on Steam and 3DMark Advanced Edition will go up from $29.99 to $34.99.
From October 12 onward, Speed Way will be included in the price when you buy 3DMark from Steam or our own online store. Since we released Time Spy in 2016, 3DMark users have enjoyed many free updates, including Time Spy Extreme, the 3DMark CPU Profile, 3DMark Wild Life, and multiple tests demonstrating new DirectX features. With the addition of Speed Way, the price of 3DMark on Steam and 3DMark Advanced Edition will go up from $29.99 to $34.99.