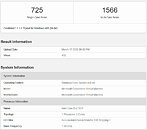
TSMC 5 nm Customers Listed, Intel Rumored to be One of Them
TSMC is working hard to bring a new 5 nm (N5 and N5+) despite all the hiccups the company may have had due to the COVID-19 pandemic happening. However, it seems like nothing can stop TSMC, and plenty of companies have already reserved some capacity for their chips. With mass production supposed to start in Q3 of this year, 5 nm node should become one of the major nodes over time for TSMC, with predictions that it will account for 10% of all capacity for 2020. Thanks to the report of ChinaTimes, we have a list of new clients for the TSMC 5 nm node, with some very interesting names like Intel appearing on the list.
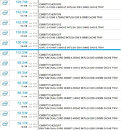
Apple and Huawei/HiSilicon will be the biggest customers for the node this year with A14 and Kirin 1000 chips being made for N5 node, with Apple ordering the A15 chips and Huawei readying the Kirin 1100 5G chip for the next generation N5+. From there, AMD will join the 5 nm party for Zen 4 processors and RDNA 3 graphics cards. NVIDIA has also reserved some capacity for its Hopper architecture, which is expected to be a consumer-oriented option, unlike Ampere. And perhaps the most interesting entry to the list is Intel Xe graphics cards. The list shows that Intel might use the N5 process form TSMC so it can ensure the best possible performance for its future cards, in case it has some issues manufacturing its own nodes, just like it did with 10 nm.
Apple and Huawei/HiSilicon will be the biggest customers for the node this year with A14 and Kirin 1000 chips being made for N5 node, with Apple ordering the A15 chips and Huawei readying the Kirin 1100 5G chip for the next generation N5+. From there, AMD will join the 5 nm party for Zen 4 processors and RDNA 3 graphics cards. NVIDIA has also reserved some capacity for its Hopper architecture, which is expected to be a consumer-oriented option, unlike Ampere. And perhaps the most interesting entry to the list is Intel Xe graphics cards. The list shows that Intel might use the N5 process form TSMC so it can ensure the best possible performance for its future cards, in case it has some issues manufacturing its own nodes, just like it did with 10 nm.