Chinese Loongson 3D5000 Features 32 Cores and is 4x Faster Than the Average Arm Chip
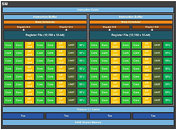
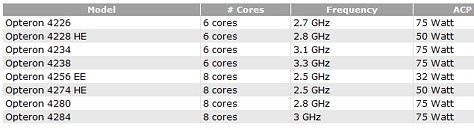
Amid the push for technology independence, Chinese companies are pushing out more products to satisfy the need for the rapidly soaring demand for domestic data processing silicon. Today, we have information that Chinese Loongson has launched a 3D5000 CPU with as many as 32 cores. Utilizing chiplet technology, the 3D5000 represents a combination of two 16-core 3C5000 processors based on LA464 cores, based on LoongArch ISA that follows the combination of RISC and MIPS ISA design principles. The new chip features 64 MB of L3 cache, supports eight-channel DDR4-3200 ECC memory achieving 50 GB/s, and has five HyperTransport (HT) 3.0 interfaces. The TDP configuration of the chip is officially 300 Watts; however, normal operation is usually at around 150 Watts, with LA464 cores running at 2 GHz.
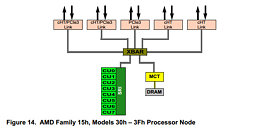
Scaling of the new chip goes beyond the chiplet, and pours over into system, as 3D5000 supports 2P and 4P configurations, where a single motherboard can become a system of up to 128 cores. To connect them, Loongson uses a 7A2000 bridge chip that is reportedly 400% faster than the previous solution, although we have no information about the last chip bridge. Based on the LGA-4129 package, the chip size is 75.4x58.5×6.5 mm. Regarding performance, Loongson compares it to the average Arm chip that goes into smartphones and claims that its designs are up to four times faster. In SPEC2006, performance reaches 425 points, while maintaining a single TeraFLOP at dual-precision 64-bit format. On the other hand, the processor was built for security, as the chip has a custom hardware-baked security to prevent Spectre and Meltdown, has an on-package Trusted Platform Module (TPM), and has a secret China-made security algorithm with an embedded custom security module that does encryption and decryption at 5 Gbps.
Scaling of the new chip goes beyond the chiplet, and pours over into system, as 3D5000 supports 2P and 4P configurations, where a single motherboard can become a system of up to 128 cores. To connect them, Loongson uses a 7A2000 bridge chip that is reportedly 400% faster than the previous solution, although we have no information about the last chip bridge. Based on the LGA-4129 package, the chip size is 75.4x58.5×6.5 mm. Regarding performance, Loongson compares it to the average Arm chip that goes into smartphones and claims that its designs are up to four times faster. In SPEC2006, performance reaches 425 points, while maintaining a single TeraFLOP at dual-precision 64-bit format. On the other hand, the processor was built for security, as the chip has a custom hardware-baked security to prevent Spectre and Meltdown, has an on-package Trusted Platform Module (TPM), and has a secret China-made security algorithm with an embedded custom security module that does encryption and decryption at 5 Gbps.