Intel Royal Core Successor Rumored to be Codenamed Cobra Core
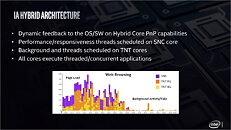
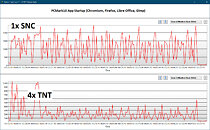
Intel's future processor microarchitectures and their constituent CPU cores have hit the rumor-mill. The "Lion Cove" P-core is now current-gen, as products based on the Core Ultra 200V "Lunar Lake" processor, which implements it, have been announced. "Lion Cove" will also be the main workhorse of "Arrow Lake," and Intel's Xeon 7 P-core server processors. The core ditches Hyper-Threading, but introduces a double-digit percent IPC gain over "Raptor Cove." The thunder of "Lion Cove" was stolen by the new "Skymont" E-core during the "Lunar Lake" technical presentations, as it offers nearly the same IPC as "Raptor Cove," at much lower power, and is held back by a lack of HTT and its inability to operate at high clock speeds that "Raptor Cove" can. We predict "Skymont" is shaking things up at Intel, and will have an impact on the way the company's future CPU cores are designed—to place greater emphasis on power and die-area to achieve IPC growth targets with each generation.
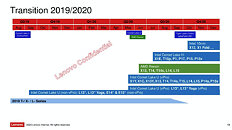
The successor to "Lion Cove" is codenamed "Royal Core." This would be the first time in over five years (since "Sunny Cove") that Intel's P-core codename doesn't use "Cove," signaling a departure from that naming scheme. The first iteration of "Royal Core" will power Intel's "Nova Lake" microarchitecture that succeeds "Lunar Lake." A slightly updated version of this core, codenamed "Royal Core 1.1," will power the "Beast Lake" microarchitecture, which likely falls in the lineage of "Arrow Lake," if not being a direct successor to it. An alleged Intel employee's work project description revealed "Cobra Core," a CPU core that succeeds "Royal Core," although the codename of its parent microarchitecture hasn't been revealed. Microarchitectures such as "Beast Lake," and its successor implementing "Cobra Core" are slated for much later into the decade, and we don't expect them to see the light of the day till at least 2026-27, if not later.
The successor to "Lion Cove" is codenamed "Royal Core." This would be the first time in over five years (since "Sunny Cove") that Intel's P-core codename doesn't use "Cove," signaling a departure from that naming scheme. The first iteration of "Royal Core" will power Intel's "Nova Lake" microarchitecture that succeeds "Lunar Lake." A slightly updated version of this core, codenamed "Royal Core 1.1," will power the "Beast Lake" microarchitecture, which likely falls in the lineage of "Arrow Lake," if not being a direct successor to it. An alleged Intel employee's work project description revealed "Cobra Core," a CPU core that succeeds "Royal Core," although the codename of its parent microarchitecture hasn't been revealed. Microarchitectures such as "Beast Lake," and its successor implementing "Cobra Core" are slated for much later into the decade, and we don't expect them to see the light of the day till at least 2026-27, if not later.