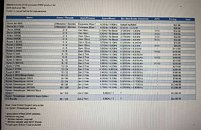
AMD Patches Zenbleed Vulnerability with AGESA 1.2.0.Ca Update
AMD classified the Zenbleed vulnerability, CVE-2023-20593, as a medium-level threat about a year ago. AMD has acknowledged that it could potentially allow an attacker to access sensitive information under certain microarchitectural circumstances. Today, MSI has released new BIOS updates featuring AMD's AM4 AGESA 1.2.0.Ca firmware update. This update addresses the Zenbleed vulnerability affecting AMD's Ryzen 4000 series Zen 2 APUs. MSI is proactively rolling out the new BIOS updates across its range of compatible motherboards. The updates are currently available for almost all X570 motherboards, with support for other chipsets and 400 series motherboards expected to follow soon.
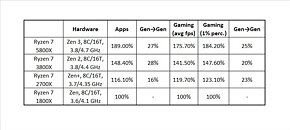
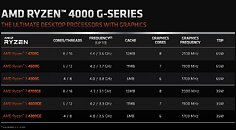
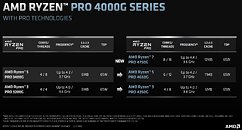
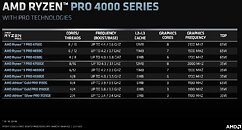
The AGESA 1.2.0.Ca firmware update specifically targets the Zenbleed vulnerability in the Zen 2 microarchitecture. Although the vulnerability primarily affects Ryzen 4000 "Renoir" APUs, it also exists in other Zen 2 processors, including the Ryzen 3000 series and certain EPYC and Threadripper CPUs. AMD has already addressed the Zenbleed vulnerability in previous AGESA microcode updates for Ryzen 3000 processors and other platforms, such as EPYC server CPUs and Ryzen mobile CPUs. However, the Ryzen Embedded V2000 CPUs are still awaiting the EmbeddedPi-FP6 1.0.0.9 AGESA firmware update, which is expected to be released by April. While AMD has not explicitly stated whether the security update will impact performance, previous testing of Zenbleed fixes has shown potential performance drops of up to 15% in certain workloads, although gaming performance remained relatively unaffected. Users with AM4 chips based on architectures other than Zen 2, such as Zen+ or Zen 3, do not need to update their BIOS as they are not affected by this specific vulnerability.
The AGESA 1.2.0.Ca firmware update specifically targets the Zenbleed vulnerability in the Zen 2 microarchitecture. Although the vulnerability primarily affects Ryzen 4000 "Renoir" APUs, it also exists in other Zen 2 processors, including the Ryzen 3000 series and certain EPYC and Threadripper CPUs. AMD has already addressed the Zenbleed vulnerability in previous AGESA microcode updates for Ryzen 3000 processors and other platforms, such as EPYC server CPUs and Ryzen mobile CPUs. However, the Ryzen Embedded V2000 CPUs are still awaiting the EmbeddedPi-FP6 1.0.0.9 AGESA firmware update, which is expected to be released by April. While AMD has not explicitly stated whether the security update will impact performance, previous testing of Zenbleed fixes has shown potential performance drops of up to 15% in certain workloads, although gaming performance remained relatively unaffected. Users with AM4 chips based on architectures other than Zen 2, such as Zen+ or Zen 3, do not need to update their BIOS as they are not affected by this specific vulnerability.