Micron HBM Designed into Leading AMD AI Platform
Micron Technology, Inc. today announced the integration of its HBM3E 36 GB 12-high offering into the upcoming AMD Instinct MI350 Series solutions. This collaboration highlights the critical role of power efficiency and performance in training large AI models, delivering high-throughput inference and handling complex HPC workloads such as data processing and computational modeling. Furthermore, it represents another significant milestone in HBM industry leadership for Micron, showcasing its robust execution and the value of its strong customer relationships.
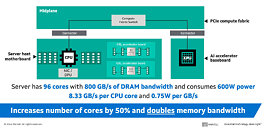
Micron HBM3E 36 GB 12-high solution brings industry-leading memory technology to AMD Instinct MI350 Series GPU platforms, providing outstanding bandwidth and lower power consumption. The AMD Instinct MI350 Series GPU platforms, built on AMD advanced CDNA 4 architecture, integrate 288 GB of high-bandwidth HBM3E memory capacity, delivering up to 8 TB/s bandwidth for exceptional throughput. This immense memory capacity allows Instinct MI350 series GPUs to efficiently support AI models with up to 520 billion parameters—on a single GPU. In a full platform configuration, Instinct MI350 Series GPUs offers up to 2.3 TB of HBM3E memory and achieves peak theoretical performance of up to 161 PFLOPS at FP4 precision, with leadership energy efficiency and scalability for high-density AI workloads. This tightly integrated architecture, combined with Micron's power-efficient HBM3E, enables exceptional throughput for large language model training, inference and scientific simulation tasks—empowering data centers to scale seamlessly while maximizing compute performance per watt. This joint effort between Micron and AMD has enabled faster time to market for AI solutions.
Micron HBM3E 36 GB 12-high solution brings industry-leading memory technology to AMD Instinct MI350 Series GPU platforms, providing outstanding bandwidth and lower power consumption. The AMD Instinct MI350 Series GPU platforms, built on AMD advanced CDNA 4 architecture, integrate 288 GB of high-bandwidth HBM3E memory capacity, delivering up to 8 TB/s bandwidth for exceptional throughput. This immense memory capacity allows Instinct MI350 series GPUs to efficiently support AI models with up to 520 billion parameters—on a single GPU. In a full platform configuration, Instinct MI350 Series GPUs offers up to 2.3 TB of HBM3E memory and achieves peak theoretical performance of up to 161 PFLOPS at FP4 precision, with leadership energy efficiency and scalability for high-density AI workloads. This tightly integrated architecture, combined with Micron's power-efficient HBM3E, enables exceptional throughput for large language model training, inference and scientific simulation tasks—empowering data centers to scale seamlessly while maximizing compute performance per watt. This joint effort between Micron and AMD has enabled faster time to market for AI solutions.