 163
163
AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT Review
Value & Conclusion »Clock Speeds
For this test, we first let the card sit in idle to reach thermal equilibrium. Next, we start a constant 100% gaming load, recording several important parameters while the test is running. This shows you the thermal behavior of the card and how the fans ramp up as temperatures increase. Once temperatures are stable (no increase for two minutes), we stop the load and record how the card cools down over time.
Pay attention to the second part of the blue curve, above "Frequency". Note how the clocks suddenly start fluctuating wildly. It seems the card encounters some kind of "throttling" condition, which is probably related to heat, and tries to keep heat output in check. Besides the obvious implications of the clock swings, what's surprising here is that the voltage gets dialed up all the way to 1.2 V from time to time—higher than when the card is running cool. Higher voltage means more heat output, which of course amplifies whatever the clocking mechanism is trying to avoid.. not a good solution.
Voltage-Frequency Analysis
For the graph below, we recorded all GPU clock and GPU voltage combinations of our 1920x1080 resolution benchmarking suite. The plotted points are transparent, which allows them to add up to indicate more often used values. A light color means the clock/voltage combination is rarely used and a dark color means it's active more often.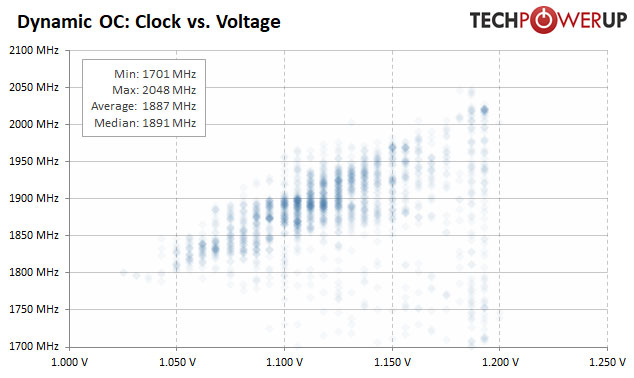
Clock Profiles
Modern graphics cards have several clock profiles that are selected to balance power draw and performance requirements.The following table lists the clock settings for important performance scenarios and the GPU voltage that is used in those states.
| GPU Clock | Memory Clock | GPU Voltage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop | 6 MHz | 100 MHz | 0.725 V |
| Multi-Monitor | 6 MHz | 871 MHz | 0.725 V |
| Media Playback | 51 MHz | 100 MHz | 0.725 V |
| 3D Load | 1701 - 2048 MHz | 1750 MHz | 1.006 - 1.200 V |
Apr 2nd, 2025 00:16 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- HIS 7870 IceQ Turbo 2GB EFI BIOS for Mac OS (0)
- Looking 4 a Solid AM5 MB? (1)
- Folding Pie and Milestones!! (9455)
- Should you physically remove secondary NVMe drives when performing a clean Windows install? (46)
- random system shutdown with fans running at full speed (14)
- Is the futureproof gaming solution a four drive system? (44)
- Help me pick a UPS (15)
- Hotspot 110° (20)
- RTX 3090 is still a good card? (29)
- PCB serial number explanation Asrock rx5700xt Taichi oc+ (8)
Popular Reviews
- DDR5 CUDIMM Explained & Benched - The New Memory Standard
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Pulse Review
- SilverStone Lucid 04 Review
- ASRock Phantom Gaming B850 Riptide Wi-Fi Review - Amazing Price/Performance
- Palit GeForce RTX 5070 GamingPro OC Review
- Gigabyte GeForce RTX 5080 Gaming OC Review
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Nitro+ Review - Beating NVIDIA
- Samsung 9100 Pro 2 TB Review - The Best Gen 5 SSD
- Assassin's Creed Shadows Performance Benchmark Review - 30 GPUs Compared
- be quiet! Pure Rock Pro 3 Black Review
Controversial News Posts
- MSI Doesn't Plan Radeon RX 9000 Series GPUs, Skips AMD RDNA 4 Generation Entirely (146)
- Microsoft Introduces Copilot for Gaming (124)
- AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT Reportedly Outperforms RTX 5080 Through Undervolting (119)
- NVIDIA Reportedly Prepares GeForce RTX 5060 and RTX 5060 Ti Unveil Tomorrow (115)
- Over 200,000 Sold Radeon RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT GPUs? AMD Says No Number was Given (100)
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5050, RTX 5060, and RTX 5060 Ti Specifications Leak (96)
- Retailers Anticipate Increased Radeon RX 9070 Series Prices, After Initial Shipments of "MSRP" Models (90)
- China Develops Domestic EUV Tool, ASML Monopoly in Trouble (88)