Tuesday, June 12th 2018

Intel Starts Testing Smallest 'Spin Qubit' Chip for Quantum Computing
Intel researchers are taking new steps toward quantum computers by testing a tiny new "spin qubit" chip. The new chip was created in Intel's D1D Fab in Oregon using the same silicon manufacturing techniques that the company has perfected for creating billions of traditional computer chips. Smaller than a pencil's eraser, it is the tiniest quantum computing chip Intel has made.
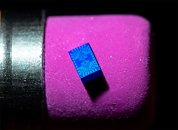
The new spin qubit chip runs at the extremely low temperatures required for quantum computing: roughly 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit - 250 times colder than space. The spin qubit chip does not contain transistors - the on/off switches that form the basis of today's computing devices - but qubits (short for "quantum bits") that can hold a single electron. The behavior of that single electron, which can be in multiple spin states simultaneously, offers vastly greater computing power than today's transistors, and is the basis of quantum computing.The zigzag lines in the photo are printed wires connecting the chip's qubits to the outside world.
One feature of Intel's tiny new spin qubit chip is especially promising. Its qubits are extraordinarily small - about 50 nanometers across and visible only under an electron microscope. About 1,500 qubits could fit across the diameter of a single human hair.
This means the design for new Intel spin qubit chip could be dramatically scaled up. Future quantum computers will contain thousands or even millions of qubits - and will be vastly more powerful than today's fastest supercomputers.
The new spin qubit chip runs at the extremely low temperatures required for quantum computing: roughly 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit - 250 times colder than space. The spin qubit chip does not contain transistors - the on/off switches that form the basis of today's computing devices - but qubits (short for "quantum bits") that can hold a single electron. The behavior of that single electron, which can be in multiple spin states simultaneously, offers vastly greater computing power than today's transistors, and is the basis of quantum computing.The zigzag lines in the photo are printed wires connecting the chip's qubits to the outside world.
One feature of Intel's tiny new spin qubit chip is especially promising. Its qubits are extraordinarily small - about 50 nanometers across and visible only under an electron microscope. About 1,500 qubits could fit across the diameter of a single human hair.
This means the design for new Intel spin qubit chip could be dramatically scaled up. Future quantum computers will contain thousands or even millions of qubits - and will be vastly more powerful than today's fastest supercomputers.


24 Comments on Intel Starts Testing Smallest 'Spin Qubit' Chip for Quantum Computing
Space or rather something like CMB ~ -270.556 Celsius
I'm not sure the math is right.
There's definitely a lot of "spin" in this.
Some tasks, like integer factoring, DNA analysis, cryptography, and modeling complicated chemical reactions require an enormous amount of operations to be completed. These are the kind of tasks that could take billions of years to complete even on the best computers. The difference is so important that, with enough qubits, billion-year operations on classical computers can take days or hours on quantum devices. This article explains why - medium.com/quantum1net/classical-computing-vs-quantum-computing-the-quantum-cracking-fest-begins-6219f899de3f[
Still the quibits are in an infant state and the computers require huge amount of liquid H2 or N2 to work. We are in the "first generation CRT TVs now"... :D