MonsterLabo Designs Giant CPU, GPU Cooler Dubbed "The Heart"
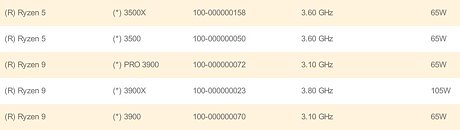
MonsterLabo, a team of four people best known for their work on "The First" PC case, are at it again with giant pieces of PC component tech. This time, they took tried and true designs and sizes of CPU and GPU coolers and threw them into an enlargement ray, coming up with what they are calling "The Heart". As it stands, and it stands higher and heavier than all other cooling solutions hitherto, "The Heart" is a cooling solution that extends from your CPU through to your GPU, cooling both with its design of densely stacked fins.
Dimensions is where "The Heart" is bold, with the cooler measuring 200 by 185 mm and 265 mm tall. Adding insult to injury, its weight comes in at 6.6 lbs (3 Kg for us metric system aficionados). MonsterLabo rates the cooler's dissipation capabilities at 100 W CPU load and a 120 W GPU. Adding a 500-RPM 140 mm fan would bump those numbers to 140 W and 160 W, respectively. Mind these numbers apply to cases where "The Heart" is installed into MonsterLabo's own The First case, but differences should be relatively minor in any other case, should you actually be able to install it there. Of course, the combined CPU and GPU design will be very hit or miss - your graphics card will have to be perfectly compatible with the cooler, with its GPU set just right on the PCB for it to be perfectly covered by it. If you want to risk that, you can always drop $200 or €180 for The Heart, in either black or white finishes. Inexpensive for a heart, yes, but extremely expensive as a cooler with expected limited compatibility.
Dimensions is where "The Heart" is bold, with the cooler measuring 200 by 185 mm and 265 mm tall. Adding insult to injury, its weight comes in at 6.6 lbs (3 Kg for us metric system aficionados). MonsterLabo rates the cooler's dissipation capabilities at 100 W CPU load and a 120 W GPU. Adding a 500-RPM 140 mm fan would bump those numbers to 140 W and 160 W, respectively. Mind these numbers apply to cases where "The Heart" is installed into MonsterLabo's own The First case, but differences should be relatively minor in any other case, should you actually be able to install it there. Of course, the combined CPU and GPU design will be very hit or miss - your graphics card will have to be perfectly compatible with the cooler, with its GPU set just right on the PCB for it to be perfectly covered by it. If you want to risk that, you can always drop $200 or €180 for The Heart, in either black or white finishes. Inexpensive for a heart, yes, but extremely expensive as a cooler with expected limited compatibility.