Intel CFO Talks About 7nm Rollout, Delay in 10nm, Increased Competition from AMD
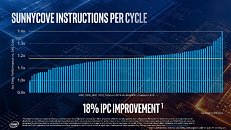
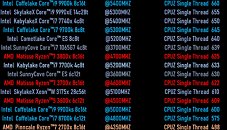
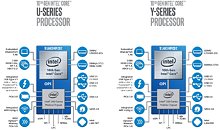
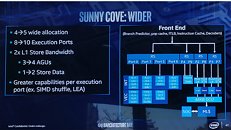
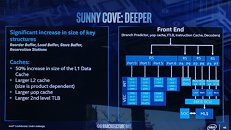
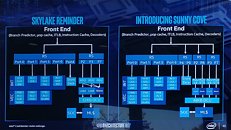
Intel CFO George Davis in an interview with Barron's commented on the company's financial health, and some of the reasons behind its rather conservative gross margin guidance looking forward to at least 2023. Intel's current product stack is moving on to the company's 10 nm silicon fabrication process in a phased manner. The company is allocating 10 nm to mobile processors and enterprise processors, while brazening it out with 14 nm on the client-desktop and HEDT platforms until they can build 10 nm desktop parts. AMD has deployed its high-IPC "Zen 2" microarchitecture on TSMC's 7 nm DUV process, with plans to go EUV in the coming months.
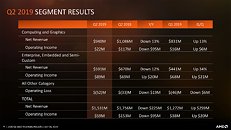
"We're still keenly focused on gross margin. Everything from capital efficiency to the way we're designing our products. What we've said though, the delay in 10 nanometer means that we're going to be a little bit disadvantaged on unit cost for a period of time. We actually gave guidance for gross margin out in 2021 to help people understand. 2023 is the period that we were ultimately guiding [when] we're going to see very strong revenue growth and margin expansion. We've got to get through this period where we have the 10 nanometer being a little bit late [as] we're not optimized on a node that we're on. But [by] then we're moving to a two to two and a half year cadence on the next nodes. So we're pulling in the spending on 7 nanometer, which will start up in the second half of 2021 because we think it's the right thing to do competitively," he said.
"We're still keenly focused on gross margin. Everything from capital efficiency to the way we're designing our products. What we've said though, the delay in 10 nanometer means that we're going to be a little bit disadvantaged on unit cost for a period of time. We actually gave guidance for gross margin out in 2021 to help people understand. 2023 is the period that we were ultimately guiding [when] we're going to see very strong revenue growth and margin expansion. We've got to get through this period where we have the 10 nanometer being a little bit late [as] we're not optimized on a node that we're on. But [by] then we're moving to a two to two and a half year cadence on the next nodes. So we're pulling in the spending on 7 nanometer, which will start up in the second half of 2021 because we think it's the right thing to do competitively," he said.