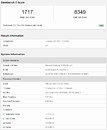
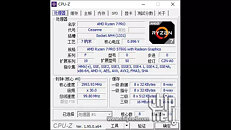
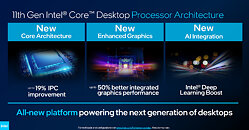
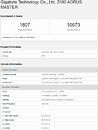
Today, Intel has decided to surprise us and give an update to its upcoming CPU lineup for desktop. With the 11th generation, Core CPUs codenamed Rocket Lake-S, Intel is preparing to launch the new lineup in the first quarter of 2021. This means that we are just a few months away from this launch. When it comes to the architecture of these new processors, they are going to be based on a special Cypress Cove design. Gone are the days of Skylake-based designs that were present from the 6th to 10th generation processors. The Cypress Cove, as Intel calls it, is an Ice Lake adaptation. Contrary to the previous rumors, it is not an adaptation of Tiger Lake Willow Cove, but rather Ice Lake Sunny Cove.
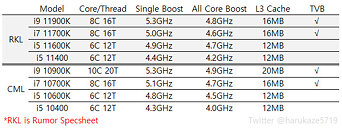
The CPU instruction per cycle (IPC) is said to grow in double-digits, meaning that the desktop users are finally going to see an improvement that is not only frequency-based. While we do not know the numbers yet, we can expect them to be better than the current 10th gen parts. For the first time on the Intel platform for desktops, we will see the adoption of PCIe 4.0 chipset, which will allow for much faster SSD speeds and support the latest GPUs, specifically, there will be 20 PCIe 4.0 lanes coming from the CPU only. The CPU will be paired with 12th generation Xe graphics, like the one found in Tiger Lake CPUs. Other technologies such as Deep Learning Boost and VNNI, Quick Sync Video, and better overclocking tuning will be present as well. Interesting thing to note here is that the 10C/20T Core i9-10900K has a PL1 headroom of 125 W, and 250 W in PL2. However, the 8C/16T Rocket Lake-S CPU also features 125 W headroom in PL1, and 250 W in PL2. This indicates that the new Cypress Cove design runs hotter than the previous generation.