First Signs of AMD Zen 3 "Vermeer" CPUs Surface, Ryzen 7 5800X Tested
AMD is preparing to launch the new iteration of desktop CPUs based on the latest Zen 3 core, codenamed Vermeer. On October 8th, AMD will hold the presentation and again deliver the latest technological advancements to its desktop platform. The latest generation of CPUs will be branded as a part of 5000 series, bypassing the 4000 series naming scheme which should follow, given that the prior generation was labeled as 3000 series of processors. Nonetheless, AMD is going to bring a new Zen 3 core with its processors, which should bring modest IPC gains. It will be manufactured on TSMC's 7 nm+ manufacturing node, which offers a further improvement to power efficiency and transistor density.
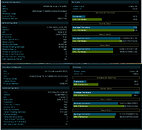
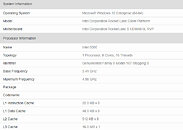
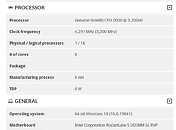
Today, we have gotten the first benchmark of AMD's upcoming Ryzen 7 5800X CPU. Thanks to the popular hardware leaker, TUP APISAK, we have the first benchmark of the new Vermeer processor, compared to Intel's latest and greatest - Core i9-10900K. The AMD processor is an eight-core, sixteen threaded model compared to the 10C/20T Intel processor. While we do not know the final clocks of the AMD CPU, we could assume that the engineering sample was used and we could see an even higher performance. Below you can see the performance of the CPU and how it compares to Intel. By the numbers shown, we can expect AMD to possibly be a new gaming king, as the numbers are very close to Intel. The average batch result for the Ryzen 7 5800X was 59.3 FPS and when it comes to CPU frames it managed to score 133.6 FPS. Intel's best managed to average 60.3 FPS and 114.8 FPS from the CPU framerates. Both systems were tested with NVIDIA's GeForce RTX 2080 GPUs.
Today, we have gotten the first benchmark of AMD's upcoming Ryzen 7 5800X CPU. Thanks to the popular hardware leaker, TUP APISAK, we have the first benchmark of the new Vermeer processor, compared to Intel's latest and greatest - Core i9-10900K. The AMD processor is an eight-core, sixteen threaded model compared to the 10C/20T Intel processor. While we do not know the final clocks of the AMD CPU, we could assume that the engineering sample was used and we could see an even higher performance. Below you can see the performance of the CPU and how it compares to Intel. By the numbers shown, we can expect AMD to possibly be a new gaming king, as the numbers are very close to Intel. The average batch result for the Ryzen 7 5800X was 59.3 FPS and when it comes to CPU frames it managed to score 133.6 FPS. Intel's best managed to average 60.3 FPS and 114.8 FPS from the CPU framerates. Both systems were tested with NVIDIA's GeForce RTX 2080 GPUs.