AMD Ryzen 8000 Series Processors Based on Zen 5 Architecture Reportedly Codenamed "Granite Ridge"
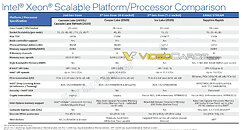
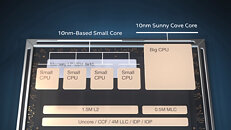
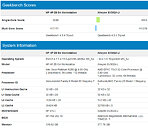
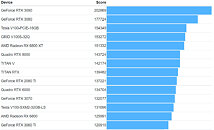
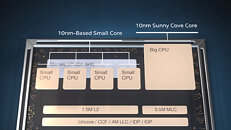
Today, we have talked about AMD's upcoming Raphael lineup of processors in the article you can find here. However, it seems like the number of leaks on AMD's plans just keeps getting greater. Thanks to the "itacg" on Weibo, we have learned that AMD's Ryzen 8000 desktop series of processors are reportedly codenamed as Granite Ridge. This new codename denotes the Zen 5 based processors, manufactured on TSMC's 3 nm (N3) node. Another piece of information is that AMD's Ryzen 8000 series APUs are allegedly called Strix Point, and they also use the 3 nm technology, along with a combination of Zen 5 and Zen 4 core design IPs. We are not sure how this exactly works out, so we have to wait to find out more.