'Spectra' Cyber Attack Breaks Coexistence Between Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Nowadays wireless technologies are increasingly sharing spectrum. This is the case for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, but also some LTE bands and harmonics. Operating on the same frequency means that these different technologies need to coordinate wireless spectrum access to avoid collisions. Especially for nearby sources, as it is the case for multiple chips within one smartphone, so-called coexistence is the key to high-performance spectrum sharing.
Coexistence between wireless chips can be implemented in various ways. While there are open specifications, most manufacturers opt to develop proprietary coexistence mechanisms to further improve performance. Open interfaces are not needed on combo chips that implement multiple wireless technologies, as the manufacturer has full control.
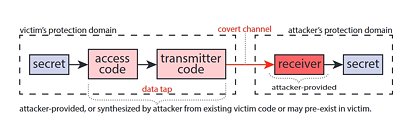
Spectra, a new vulnerability class, relies on the fact that transmissions happen in the same spectrum and wireless chips need to arbitrate the channel access. While coexistence should only increase performance, it also poses a powerful side channel.
Coexistence between wireless chips can be implemented in various ways. While there are open specifications, most manufacturers opt to develop proprietary coexistence mechanisms to further improve performance. Open interfaces are not needed on combo chips that implement multiple wireless technologies, as the manufacturer has full control.
Spectra, a new vulnerability class, relies on the fact that transmissions happen in the same spectrum and wireless chips need to arbitrate the channel access. While coexistence should only increase performance, it also poses a powerful side channel.