Intel Core i5-L16G7 is the first "Lakefield" SKU Appearance, Possible Prelude to New Nomenclature?
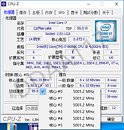
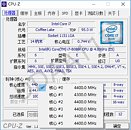
Intel Core i5-L16G7 is the first commercial SKU that implements Intel's "Lakefield" heterogenous x86 processor architecture. This 5-core chip features one high-performance "Sunny Cove" CPU core, and four smaller "Tremont" low-power cores, with an intelligent scheduler balancing workloads between the two core types. This is essentially similar to ARM big.LITTLE. The idea being that the device idles most of the time, when lower-powered CPU cores can hold the fort; performance cores kick in only when really needed, until which time they remain power-gated. Thai PC enthusiast TUM_APISAK discovered the first public appearance of the i5-L16G7 in an unreleased Samsung device that has the Userbenchmark device ID string "SAMSUNG_NP_767XCL."
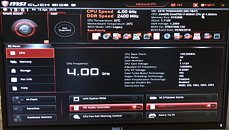
Clock speeds of the processor are listed as "1.40 GHz base, with 1.75 GHz turbo," but it's possible that the two core types have different clock-speed bands, just like the cores on big.LITTLE SoCs. Other key components of "Lakefield" include an iGPU based on the Gen11 graphics architecture, and an LPDDR4X memory controller. "Lakefield" implements Foveros packaging, in which high-density component dies based on newer silicon fabrication nodes are integrated with silicon interposers based on older fabrication processes, which facilitate microscopic high-density wiring between the dies. In case of "Lakefield," the Foveros package features a 10 nm "compute field" die sitting atop a 22 nm "base field" interposer.
Clock speeds of the processor are listed as "1.40 GHz base, with 1.75 GHz turbo," but it's possible that the two core types have different clock-speed bands, just like the cores on big.LITTLE SoCs. Other key components of "Lakefield" include an iGPU based on the Gen11 graphics architecture, and an LPDDR4X memory controller. "Lakefield" implements Foveros packaging, in which high-density component dies based on newer silicon fabrication nodes are integrated with silicon interposers based on older fabrication processes, which facilitate microscopic high-density wiring between the dies. In case of "Lakefield," the Foveros package features a 10 nm "compute field" die sitting atop a 22 nm "base field" interposer.