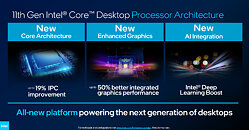
Intel Readies Xeon W-1300 Socket LGA1200 Processors Based on "Rocket Lake"
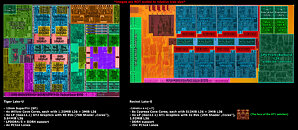
Intel is reportedly giving final touches to the Xeon W-1300 line of enterprise processors targeting workstations, according to an ASRock CPU support list dug up by Komachi Ensaka. The processors are based on the same 14 nm "Rocket Lake" silicon as the company's 11th Gen Core desktop processors, and come in core counts of up to 8-core/16-thread. The lineup is expected to debut with five SKUs, three of which are 8-core/16-thread, and two 6-core/12-thread.
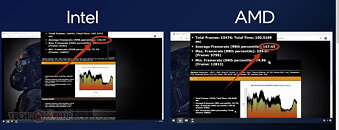
The lineup is led by the W-1370, with base frequency of 2.90 GHz, 16 MB of shared L3 cache, and 80 W TDP. Next up, is the slightly slower W-1390, clocked at 2.80 GHz, and 80 W TDP. The third 8-core part is the W-1390T, which is clocked at just 1.50 GHz (base), and comes with aggressive power-management that gives it a TDP rating of 35 W. The 6-core/12-thread W-1350P has the highest clock speeds, with a base frequency of 4.00 GHz, 12 MB of shared L3 cache, and 125 W TDP. The W-1350 is its slower sibling, clocked at 3.30 GHz, and 80 W TDP. The processors will be compatible with Intel Z490, W480, and H470 chipsets, besides their 500-series successors.
The lineup is led by the W-1370, with base frequency of 2.90 GHz, 16 MB of shared L3 cache, and 80 W TDP. Next up, is the slightly slower W-1390, clocked at 2.80 GHz, and 80 W TDP. The third 8-core part is the W-1390T, which is clocked at just 1.50 GHz (base), and comes with aggressive power-management that gives it a TDP rating of 35 W. The 6-core/12-thread W-1350P has the highest clock speeds, with a base frequency of 4.00 GHz, 12 MB of shared L3 cache, and 125 W TDP. The W-1350 is its slower sibling, clocked at 3.30 GHz, and 80 W TDP. The processors will be compatible with Intel Z490, W480, and H470 chipsets, besides their 500-series successors.