AMD Ryzen 3000 and Older Zen Chips Don't Support SAM Due to Hardware Limitation, Intel Chips Since Haswell Support it
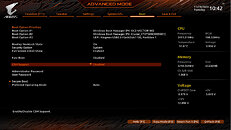
AMD Ryzen 3000 "Matisse" processors based on the "Zen 2" microarchitecture, as well as older AMD processors based on "Zen+" and "Zen" microarchitectures, do not support the company's Smart Access Memory (SAM) feature being introduced with Radeon RX 6000 series graphics cards. SAM is essentially a branding of the Resizable Base-Address Register (Resizable-BAR) feature developed by the PCI-SIG; which enables a processor to see a graphics card's entire video memory as a single addressable block, rather than through 256-megabyte apertures. Apparently the PCI-Express root complex of Ryzen 5000 "Vermeer" processors introduce an instruction called full-rate _pdep_u32/64, which is required for resizable-BAR to work.
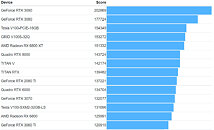
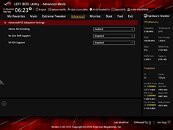
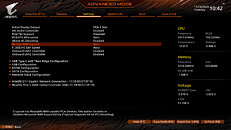
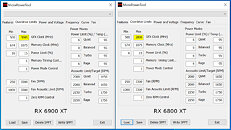
It gets more interesting—Intel processors have been supporting this feature since the company's 4th Gen Core "Haswell," which introduced it with its 20-lane PCI-Express gen 3.0 root-complex. This means that every Intel processor dating back to 2014 can technically support Resizable-BAR, and it's just a matter of motherboard vendors releasing UEFI firmware updates for their products (i.e. Intel 8-series chipsets and later). AMD extensively advertises SAM as adding a 1-2% performance boost to Radeon RX 6800 series graphics cards. Since this is a PCI-SIG feature, NVIDIA plans to add support for it on some of its GPUs, too. Meanwhile, in addition to AMD 500-series chipsets, even certain Intel 400-series chipset motherboards started receiving Resizable BAR support through firmware updates.
It gets more interesting—Intel processors have been supporting this feature since the company's 4th Gen Core "Haswell," which introduced it with its 20-lane PCI-Express gen 3.0 root-complex. This means that every Intel processor dating back to 2014 can technically support Resizable-BAR, and it's just a matter of motherboard vendors releasing UEFI firmware updates for their products (i.e. Intel 8-series chipsets and later). AMD extensively advertises SAM as adding a 1-2% performance boost to Radeon RX 6800 series graphics cards. Since this is a PCI-SIG feature, NVIDIA plans to add support for it on some of its GPUs, too. Meanwhile, in addition to AMD 500-series chipsets, even certain Intel 400-series chipset motherboards started receiving Resizable BAR support through firmware updates.