AMD "Renoir" APU to Support LPDDR4X Memory and New Display Engine
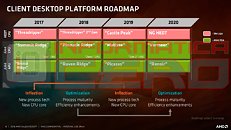
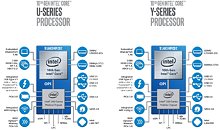
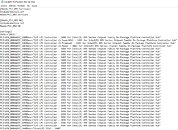
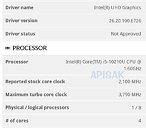
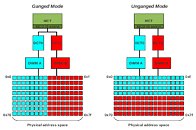
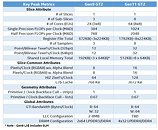
AMD's next-generation "Renoir" APU, which succeeds the company's 12 nm "Picasso," will be the company's truly next-generation chip to feature an integrated graphics solution. It's unclear as of now, if the chip will be based on a monolithic die, or if it will be a multi-chip module of a 7 nm "Zen 2" chiplet paired with an enlarged I/O controller die that has the iGPU. We're getting confirmation on two key specs - one, that the iGPU will be based on the older "Vega" graphics architecture, albeit with an updated display engine to support the latest display standards; and two, that the processor's memory controller will support the latest LPDDR4X memory standard, at speeds of up to 4266 MHz DDR. In comparison, Intel's "Ice Lake-U" chip supports LPDDX4X up to 3733 MHz.
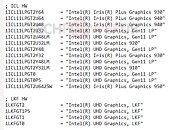
Code-lines pointing toward "Vega" graphics with an updated display controller mention the new DCN 2.1, found in AMD's new "Navi 10" GPU. This controller supports resolutions of up to 8K, DSC 1.2a, and new resolutions of 4K up to 240 Hz and 8K 60 Hz over a single cable, along with 30 bits per pixel color. The multimedia engine is also suitably updated to VCN 2.1 standard, and provides hardware-accelerated decoding for some of the newer video formats, such as VP9 and H.265 at up to 90 fps at 4K, and 8K up to 24 fps, and H.264 up to 150 fps at 4K. There's no word on when "Renoir" comes out, but a 2020 International CES unveil is likely.
Code-lines pointing toward "Vega" graphics with an updated display controller mention the new DCN 2.1, found in AMD's new "Navi 10" GPU. This controller supports resolutions of up to 8K, DSC 1.2a, and new resolutions of 4K up to 240 Hz and 8K 60 Hz over a single cable, along with 30 bits per pixel color. The multimedia engine is also suitably updated to VCN 2.1 standard, and provides hardware-accelerated decoding for some of the newer video formats, such as VP9 and H.265 at up to 90 fps at 4K, and 8K up to 24 fps, and H.264 up to 150 fps at 4K. There's no word on when "Renoir" comes out, but a 2020 International CES unveil is likely.