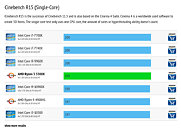
AMD Ryzen 8000 "Granite Ridge" Zen 5 Processor to Max Out at 16 Cores
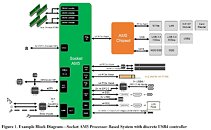
AMD's next-generation Ryzen 8000 "Granite Ridge" desktop processor based on the "Zen 5" microarchitecture, will continue to top out at 16-core/32-thread as the maximum CPU core-count possible, says a report by PC Games Hardware. The processor will retain the chiplet design of the current Ryzen 7000 "Raphael" processor, with two 8-core "Zen 5" CCDs, and one I/O die. It's very likely that AMD will reuse the same 6 nm client I/O die (cIOD) as "Raphael," just the way it used the same 12 nm cIOD between Ryzen 3000 "Matisse" and Ryzen 5000 "Vermeer;" but with updates that could enable higher DDR5 memory speeds. Each of the up to two "Eldora" Zen 5 CCDs has 8 CPU cores, with 1 MB of dedicated L2 cache per core, and 32 MB of shared L3 cache. The CCDs are very likely to be built on the TSMC 3 nm EUV silicon fabrication process.
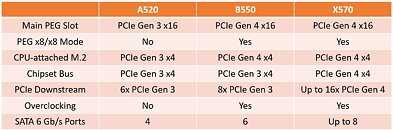
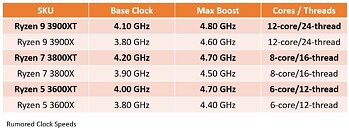
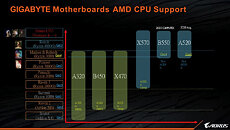
Perhaps the most interesting aspect of the PCGH leak would have to be the TDP numbers being mentioned, which continue to show higher-performance SKUs with 170 W TDP, and lower tiers with 65 W TDP. With its CPU core-counts not seeing increases, AMD would bank on not just the generational IPC increase of its "Zen 5" cores, but also max out performance within the power envelope of the new node, by dialing up clock speeds. AMD could ride out 2023 with its Ryzen 7000 "Zen 4" processors on the desktop platform, with "Granite Ridge" slated to enter production only by Q1-2024. The company could update its product stack in the meantime, perhaps even bring the 4 nm "Phoenix" monolithic APU silicon to the Socket AM5 desktop platform. Ryzen 8000 is expected to retain full compatibility with existing Socket AM5, and AMD 600-series chipset motherboards.
Perhaps the most interesting aspect of the PCGH leak would have to be the TDP numbers being mentioned, which continue to show higher-performance SKUs with 170 W TDP, and lower tiers with 65 W TDP. With its CPU core-counts not seeing increases, AMD would bank on not just the generational IPC increase of its "Zen 5" cores, but also max out performance within the power envelope of the new node, by dialing up clock speeds. AMD could ride out 2023 with its Ryzen 7000 "Zen 4" processors on the desktop platform, with "Granite Ridge" slated to enter production only by Q1-2024. The company could update its product stack in the meantime, perhaps even bring the 4 nm "Phoenix" monolithic APU silicon to the Socket AM5 desktop platform. Ryzen 8000 is expected to retain full compatibility with existing Socket AM5, and AMD 600-series chipset motherboards.