Kingston Introduces Entry-level A1000 NVMe PCIe SSD
Kingston Digital, Inc., the Flash memory affiliate of Kingston Technology Company, Inc., a world leader in memory products and technology solutions, today announced A1000 PCIe NVMe SSD. The M.2 drive is Kingston's first entry-level consumer-grade PCIe NVMe SSD utilizing 3D NAND. The A1000 delivers twice the performance of SATA at near SATA pricing.
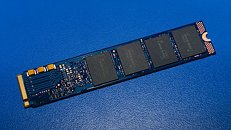
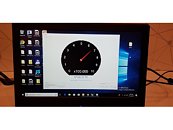
The single-sided M.2 2280 (22mm x 80mm) form factor makes A1000 ideal for notebooks and systems with limited space. The PCIe NVMe drive features a Gen 3.0 x2 interface, 4-channel Phison 5008 controller, and 3D NAND Flash. It delivers 2x the performance of SATA SSDs with read/write speed up to 1500MB/s and 1000MB/s giving it exceptional responsiveness and ultra-low latency.
The single-sided M.2 2280 (22mm x 80mm) form factor makes A1000 ideal for notebooks and systems with limited space. The PCIe NVMe drive features a Gen 3.0 x2 interface, 4-channel Phison 5008 controller, and 3D NAND Flash. It delivers 2x the performance of SATA SSDs with read/write speed up to 1500MB/s and 1000MB/s giving it exceptional responsiveness and ultra-low latency.