ORIGIN PC Unveils PRIME: The Ultimate Mid-Tower ATX Case for Elite Performance
ORIGIN PC, the ultimate ally for gamers, creators, and for those who need a premium high-performance experience, is thrilled to announce the launch of the PRIME, a revolutionary mid-tower ATX case designed to elevate performance for elite gamers, content creators, and AI professionals. Available in two versions, MILLENNIUM with AIO cooling and GENESIS with open-loop cooling for both CPU and GPU, this system promises unparalleled thermal efficiency and maximum power.
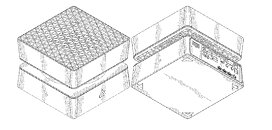
Elevate your performance with PRIME, a mid-tower ATX case crafted for elite gamers, content creators, and AI professionals. Featuring Hydro X open-loop CPU and GPU cooling, choose your color of coolant and tubing, GENESIS ensures unparalleled thermal efficiency for maximum power and reliability. MILLENNIUM offers AIO liquid cooling support ensuring efficient heat dissipation, quieter operation and peak thermal performance, making it perfect for even the most demanding builds. With support for up to Intel Core Ultra 9 series or AMD RYZEN 9000 series CPUs, this powerhouse is built to excel in demanding workloads. Its modern, sleek design is complemented by striking glass front and side panels, customizable I/O port placement, dynamic RGB lighting, and personalized UV printing. PRIME also features next-gen DDR5 memory, expandable storage, delivering unmatched speed, versatility, and style. Redefine innovation and achieve more with PRIME.
Elevate your performance with PRIME, a mid-tower ATX case crafted for elite gamers, content creators, and AI professionals. Featuring Hydro X open-loop CPU and GPU cooling, choose your color of coolant and tubing, GENESIS ensures unparalleled thermal efficiency for maximum power and reliability. MILLENNIUM offers AIO liquid cooling support ensuring efficient heat dissipation, quieter operation and peak thermal performance, making it perfect for even the most demanding builds. With support for up to Intel Core Ultra 9 series or AMD RYZEN 9000 series CPUs, this powerhouse is built to excel in demanding workloads. Its modern, sleek design is complemented by striking glass front and side panels, customizable I/O port placement, dynamic RGB lighting, and personalized UV printing. PRIME also features next-gen DDR5 memory, expandable storage, delivering unmatched speed, versatility, and style. Redefine innovation and achieve more with PRIME.