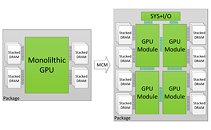
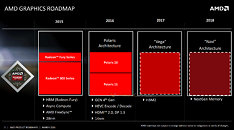
AMD "Navi" GPU Architecture Successor Codenamed "Arcturus"?
Arcturus is the fourth brightest star in the night sky, and could be the a new GPU architecture by AMD succeeding "Navi," according to a Phoronix report. The codename of Navi-successor has long eluded AMD's roadmap slides. The name "Arcturis" surfaced on Phoronix community forums, from a post by an AMD Linux liaison who is a member there. The codename is also supported by the fact that AMD is naming its GPU architectures after the brightest stars in the sky (albeit in a descending order of their brightness). Polaris is the brightest, followed by Vega, Navi, and Arcturus.
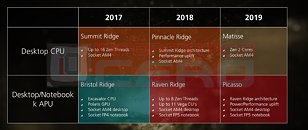
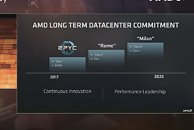
AMD last referenced the Navi-successor on a roadmap slide during its 2017 Financial Analyst Day presentation by Mark Papermaster. That slide mentioned "Vega" to be built on two silicon fabrication processes, 14 nm and "14 nm+." We know now that AMD intends to build a better-endowed "Vega" chip on 7 nm, which could be the world's first 7 nm GPU. "Navi" is slated to be built on 7 nm as the process becomes more prevalent in the industry. The same slide mentions Navi-successor as being built on "7 nm+," which going by convention, could refer to an even more advanced process than 7 nm. Unfortunately, even in 2017, when the industry was a touch more optimistic about 7 nm, AMD expected the Navi-successor to only come out by 2020. We're not holding our breath.
AMD last referenced the Navi-successor on a roadmap slide during its 2017 Financial Analyst Day presentation by Mark Papermaster. That slide mentioned "Vega" to be built on two silicon fabrication processes, 14 nm and "14 nm+." We know now that AMD intends to build a better-endowed "Vega" chip on 7 nm, which could be the world's first 7 nm GPU. "Navi" is slated to be built on 7 nm as the process becomes more prevalent in the industry. The same slide mentions Navi-successor as being built on "7 nm+," which going by convention, could refer to an even more advanced process than 7 nm. Unfortunately, even in 2017, when the industry was a touch more optimistic about 7 nm, AMD expected the Navi-successor to only come out by 2020. We're not holding our breath.