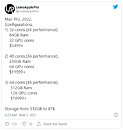
Alleged Apple M2 Max Performance Figures Show Almost 20% Single-Core Improvement
Apple's ongoing pursuit of leading performance in custom silicon packages continues with each new generation of Apple Silicon. Today, we have alleged Geekbench performance figures of the upcoming M2 Max chip, designed for the upcoming Mac devices. Featuring the same configuration with two E-cores and eight P-cores, the chip is rumored to utilize TSMC's 3 nm design. However, that is yet to be confirmed by Apple, so we don't have the exact information. In the GB5 single-thread test, the CPU set a single-core performance target of 1899 points, while the multi-core score was 8737. While last year's M1 Max chips can reach 1787 single-core and 12826 multi-core scores, these configurations are benchmarked in a Mac Studio, which has better cooling and allows for higher clocks to be achieved.
Apples to apples (pun intended) comparison with the M1 Max chip inside of a MacBook Pro version with presumably the same cooling capacity, which gets 1497 single-core and 11506 multi-core score, the new M2 Max chip is 19.4% faster in single-core results. Multi-core improvements should follow, and this M2 Max result should be different from the final product. We await more benchmarks to confirm this performance increase and the correct semiconductor manufacturing node.
Apples to apples (pun intended) comparison with the M1 Max chip inside of a MacBook Pro version with presumably the same cooling capacity, which gets 1497 single-core and 11506 multi-core score, the new M2 Max chip is 19.4% faster in single-core results. Multi-core improvements should follow, and this M2 Max result should be different from the final product. We await more benchmarks to confirm this performance increase and the correct semiconductor manufacturing node.