Intel Facing HEDT Chipset Troubles, Again?
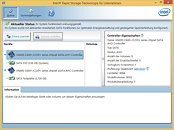
In what is a repeat of the design issues Intel faced with its previous X79 Express chipset, over its integrated storage controller, leading to motherboard vendors redesigning their products with fewer SATA/SAS ports than the platform is capable of, the company is facing design troubles with its already-launched X99 Express chipset, which drives its latest Core i7-5xxx "Haswell-E" HEDT platform. Intel X99 Express is based on a common silicon, on which the company's enterprise C610 chipset is also based. On paper, it features as many as ten SATA 6 Gb/s ports. The storage controller has its own exclusive Rapid Storage Technology driver, marked "RSTe" on Intel's Download website.
Intel withdrew version 4.1.0.1046 of its RSTe drivers (even from the list of older drivers), and made its motherboard partners do the same. Replying to German publication Heise.de, ASUS explained that the driver was withdrawn because it doesn't support ATA TRIM command for SSDs striped in a RAID 0 array. The latest driver makes only six out of ten SATA 6 Gb/s ports visible to the operating system, and you can create RAID arrays using on these six ports. The other four ports become visible as part of a separate controller, only when a device is plugged into them. This controller is recognized by Windows' internal Standard AHCI controller driver. This also means that the four ports don't benefit from the SATA power management features the first six ports do, nor can they be part of a RAID array with drives plugged to the first six ports. Intel did not respond to the Heise article.
Intel withdrew version 4.1.0.1046 of its RSTe drivers (even from the list of older drivers), and made its motherboard partners do the same. Replying to German publication Heise.de, ASUS explained that the driver was withdrawn because it doesn't support ATA TRIM command for SSDs striped in a RAID 0 array. The latest driver makes only six out of ten SATA 6 Gb/s ports visible to the operating system, and you can create RAID arrays using on these six ports. The other four ports become visible as part of a separate controller, only when a device is plugged into them. This controller is recognized by Windows' internal Standard AHCI controller driver. This also means that the four ports don't benefit from the SATA power management features the first six ports do, nor can they be part of a RAID array with drives plugged to the first six ports. Intel did not respond to the Heise article.