Intel "Willow Cove" Core, Xe LP iGPU, and "Tiger Lake" SoC Detailed
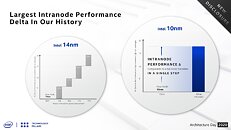
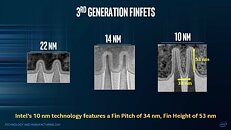
A lot is riding for Intel on its 11th Gen Core "Tiger Lake" system-on-chip (SoC), which will launch exclusively on mobile platforms, hoping to dominate the 7 W thru 15 W ultraportable form-factors in 2020, while eventually scaling up to the 25 W thru 45 W H-segment form-factors in 2021, with a variant that is rumored to double core-counts. The chip is built on Intel's new 10 nm SuperFin silicon fabrication node that enables a double digit percentage energy efficiency growth over 10 nm, allowing Intel to significantly dial up clock speeds without impacting the power envelope. The CPU and iGPU make up the two key components of the "Tiger Lake" SoC.
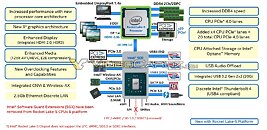
The CPU component on the "Tiger Lake" processors that launch in a few weeks from now features four "Willow Cove" CPU cores. Coupled with HyperThreading, this ends up being a 4-core/8-thread setup, although much of Intel's innovation is in giving these cores significant IPC increases over the "Skylake" core powering "Comet Lake" processors, and compared to the "Sunny Cove" cores powering "Ice Lake" a minor IPC (although major net performance increase from clock speeds). The "Willow Cove" CPU core appears to be a derivative of the "Sunny Cove" core, designed to take advantage of the 10 nm SuperFin node, along with three key innovations.
The CPU component on the "Tiger Lake" processors that launch in a few weeks from now features four "Willow Cove" CPU cores. Coupled with HyperThreading, this ends up being a 4-core/8-thread setup, although much of Intel's innovation is in giving these cores significant IPC increases over the "Skylake" core powering "Comet Lake" processors, and compared to the "Sunny Cove" cores powering "Ice Lake" a minor IPC (although major net performance increase from clock speeds). The "Willow Cove" CPU core appears to be a derivative of the "Sunny Cove" core, designed to take advantage of the 10 nm SuperFin node, along with three key innovations.