AMD is preparing to surprise Intel with its 3rd generation Ryzen Threadripper processors derived from the "Rome" MCM (codenamed "Castle Peak" for the client-platform), that features up to 64 CPU cores, a monolithic 8-channel DDR4 memory interface, and 128 PCIe gen 4.0 lanes. For the HEDT platform, AMD could reconfigure the I/O controller die for two distinct sub-platforms within HEDT - one targeting gamers/enthusiasts, and another targeting the demographic that buys Xeon W processors, including the W-3175X. The gamer/enthusiast-targeted processor line could feature a monolithic 4-channel DDR4 memory interface, and 64 PCI-Express gen 4.0 lanes from the processor socket, and additional lanes from the chipset; while the workstation-targeted processor line could essentially be EPYCs, with a wider memory bus width and more platform PCIe lanes; while retaining drop-in backwards-compatibility with AMD X399 (at the cost of physically narrower memory and PCIe I/O).
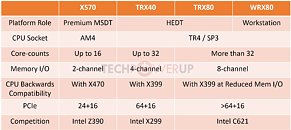
To support this diverse line of processors, AMD is coming up with not one, but three new chipsets: TRX40, TRX80, and WRX80. The TRX40 could have a lighter I/O feature-set (similar to the X570), and probably 4-channel memory on the motherboards. The TRX80 and WRX80 could leverage the full I/O of the "Rome" MCM, with 8-channel memory and more than 64 PCIe lanes. We're not sure what differentiates the TRX80 and WRX80, but we believe motherboards based on the latter will resemble proper workstation boards in form-factors such as SSI, and be made by enterprise motherboard manufacturers such as TYAN. The chipsets made their way to the USB-IF for certification, and were sniffed out by momomo_us. ASUS is ready with its first motherboards based on the TRX40, the Prime TRX40-Pro, and the ROG Strix TRX40-E Gaming.