Arm Takes Aim at Laptops: Cortex-A78C Processor for PCs Introduced
In the past few years, the Windows-on-Arm (WoA) market has gotten some momentum has with companies trying to develop their WoA PCs, primarily laptops. One example of that is Microsoft. The company has launched a Surface notebook powered by a custom chip from Snapdragon, called Surface Pro X. This device is being powered by the Snapdragon SQ2 processor. However, what seemed to be missing for a while was the lack of support from the Arm itself for this type of market. That is what the company decided to change and make a brand new processor IP dedicated to "on-the-go" devices as they call it, translating into laptops.
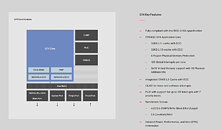
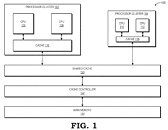
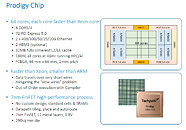
The Cortex-A78C is a new design direction which Arm thinks is a good way for laptops, to get some more serious work done. Unlike the regular Cortex-A78 which is a heterogeneous design of big and little cores (Arm's famous big.LITTLE architecture), the new Cortex-A78C revision aims to change that. The "C" version of the processor is actually a homogeneous structure made up of all the big cores. Where you would typically use four big and four little cores for a design, Arm has decided to go all big with this design. For multithreaded purposes, this is the right decision to boost performance. The level three (L3) cache has seen a boost as well, translating to 8 MB of L3$ found on the die. We are eagerly awaiting to see the first designs based on this configuration and see how it performs.
The Cortex-A78C is a new design direction which Arm thinks is a good way for laptops, to get some more serious work done. Unlike the regular Cortex-A78 which is a heterogeneous design of big and little cores (Arm's famous big.LITTLE architecture), the new Cortex-A78C revision aims to change that. The "C" version of the processor is actually a homogeneous structure made up of all the big cores. Where you would typically use four big and four little cores for a design, Arm has decided to go all big with this design. For multithreaded purposes, this is the right decision to boost performance. The level three (L3) cache has seen a boost as well, translating to 8 MB of L3$ found on the die. We are eagerly awaiting to see the first designs based on this configuration and see how it performs.