TSMC to Build Specialty Technology Fab in Japan with Sony as Minority Partner
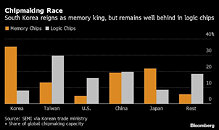
TSMC (TWSE: 2330, NYSE: TSM) and Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation ("SSS") today jointly announced that TSMC will establish a subsidiary, Japan Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing, Inc. ("JASM"), in Kumamoto, Japan to provide foundry service with initial technology of 22/28-nanometer processes to address strong global market demand for specialty technologies, with SSS participating as a minority shareholder.
Construction of JASM's fab in Japan is scheduled to begin in the 2022 calendar year with production targeted to begin by the end of 2024. The fab is expected to directly create about 1,500 high-tech professional jobs and to have a monthly production capacity of 45,000 12-inch wafers. The initial capital expenditure is estimated to be approximately US$7 billion with strong support from the Japanese government.
Under definitive agreements reached between TSMC and SSS, SSS plans to make an equity investment in JASM of approximately US $0.5 billion, which will represent a less than 20% equity stake in JASM. The closing of the transaction between TSMC and SSS is subject to customary closing conditions.
Construction of JASM's fab in Japan is scheduled to begin in the 2022 calendar year with production targeted to begin by the end of 2024. The fab is expected to directly create about 1,500 high-tech professional jobs and to have a monthly production capacity of 45,000 12-inch wafers. The initial capital expenditure is estimated to be approximately US$7 billion with strong support from the Japanese government.
Under definitive agreements reached between TSMC and SSS, SSS plans to make an equity investment in JASM of approximately US $0.5 billion, which will represent a less than 20% equity stake in JASM. The closing of the transaction between TSMC and SSS is subject to customary closing conditions.