TSMC Expects Most 7nm Customers to Move to 6nm Density
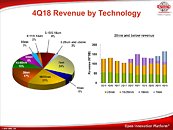
TSMC in its quarterly earnings call expressed confidence in that most of its 7 nm (N7) process production node customers would be looking to make the transition to their 6 nm (N6) process. In fact, the company expects that node to become the biggest target for volume ordering (and thus production) amongst its customers, since the new N6 fabrication technology will bring about a sort of "backwards compatibility" with design tools and semiconductor designs that manufacturers have already invested in for its N7 node, thus allowing for cost savings for its clients.
This is despite TSMC's N6 process being able to take advantage of extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) to lower manufacturing complexity. This lowering is achieved by the fact that less exposures of the silicon are required for multi-patterning - which is needed today as TSMC's N7 uses solely deep ultraviolet (DUV) lithography. Interestingly, TSMC expects other clients to pick up its N7+ manufacturing node that aren't already using their 7nm node - the need to develop new tools and lesser design compatibility between its N7 and N7+ nodes compared no N7 and N6 being the justification. TSMC's N7+ will be the first node to leverage EUV, using up to four EUVL layers, while N6 expands it up to five layers, and the upcoming N5 cranks EUVL up to fourteen (allowing for 14 layers.)
This is despite TSMC's N6 process being able to take advantage of extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) to lower manufacturing complexity. This lowering is achieved by the fact that less exposures of the silicon are required for multi-patterning - which is needed today as TSMC's N7 uses solely deep ultraviolet (DUV) lithography. Interestingly, TSMC expects other clients to pick up its N7+ manufacturing node that aren't already using their 7nm node - the need to develop new tools and lesser design compatibility between its N7 and N7+ nodes compared no N7 and N6 being the justification. TSMC's N7+ will be the first node to leverage EUV, using up to four EUVL layers, while N6 expands it up to five layers, and the upcoming N5 cranks EUVL up to fourteen (allowing for 14 layers.)